

The Atlas Centre at RAL houses the Joint Research Councils Cray X-MP/48 supercomputer which is available to members of the UK academic community through the Councils or the British Academy. The Centre also provides an IBM mainframe computing service used mainly in support of SERC scientific programmes and there are other specific activities in networking, information management and support of the computing infrastructure of SERC.
The Cray service began in 1987 and has been operating near full capacity throughout the year. There is a substantial body of scientific achievement attributable directly to use of the machine.
The major event for the IBM service was the installation of an IBM 3090 200E computer with a vector facility. This replaced two older computers which had supported the service since the early 1980s. The new machine provides an excellent base from which the service can proceed using modern technology and software.
During the year IBM announced that it had selected RAL as a participant in its European Supercomputing Initiative. It is expected that this will result in the power and the vector processing capability of the IBM facilities being substantially enhanced in the next year.
The Cray service is in its second year of operation. Since most of the awards for use of the Cray last for three years it is a little early to give a comprehensive review of scientific advances made as a result of using the supercomputer but by October 151 papers had been published in or submitted to refereed journals. A report on the scientific programme is in preparation. The following is a list of highlights which illustrates the breadth of work in progress.
Protein Crystallography Simulated annealing and molecular dynamics have been used to speed the refinement of experimental crystallographic data. A 3.3 A resolution structure of rabbit serum transferrin shows for the first time the peptide chains connecting the halves of the bi-lobal molecule.
Bioreductive Drug Design The fact that cancer cells have a reduced blood supply is being exploited by designing chemotherapeutic drugs which are active only when reduced.
Environmental Sciences The Cray is providing new, detailed models of the Antarctic Ocean, the North Sea, the upper atmosphere and global meteorology.
Epidemiology The power of the Cray makes it possible to construct bias-free analyses of the clustering and geographical distribution of certain human cancers.
Computational Fluid Dynamics New insights into the fundamental behaviour of turbulent fluids are being gained by sophisticated numerical modelling.
Structural Engineering Detailed models have been constructed for the elastic plastic behaviour and crack propagation in the steel walls of PWR pressure vessels.
Atomic Physics The power of all four Cray processors has been used to extend the range of atoms which can be modelled and to increase the accuracy of atomic collision cross sections.
Particle Accelerator Physics Previous objections to the use of lasers to drive high field particle accelerators have been removed by the discovery of a new nonlinear self-focusing effect.
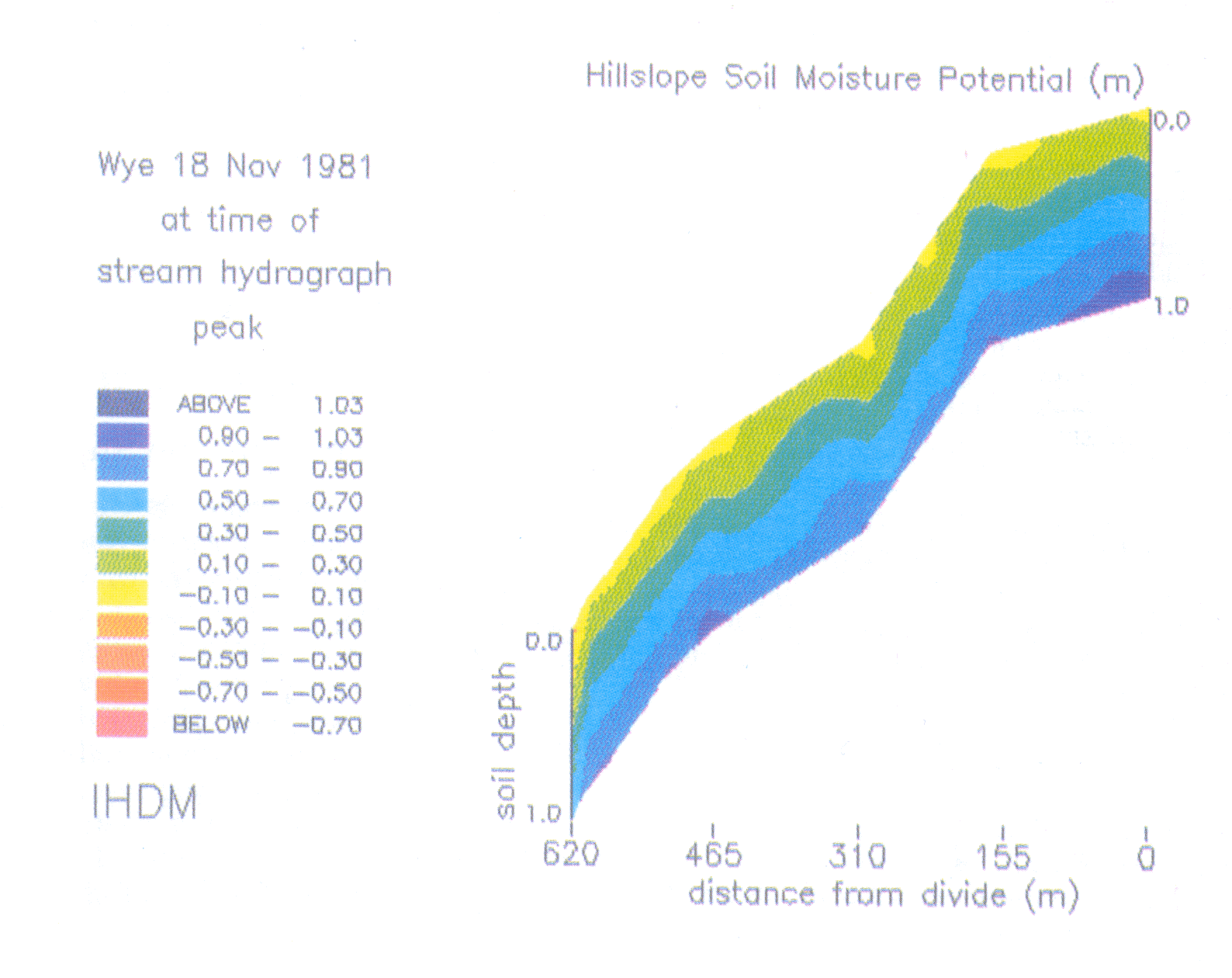
Hydrology Storm water runoff and soil moisture in the Wye valley have been simulated (Fig 5.1).
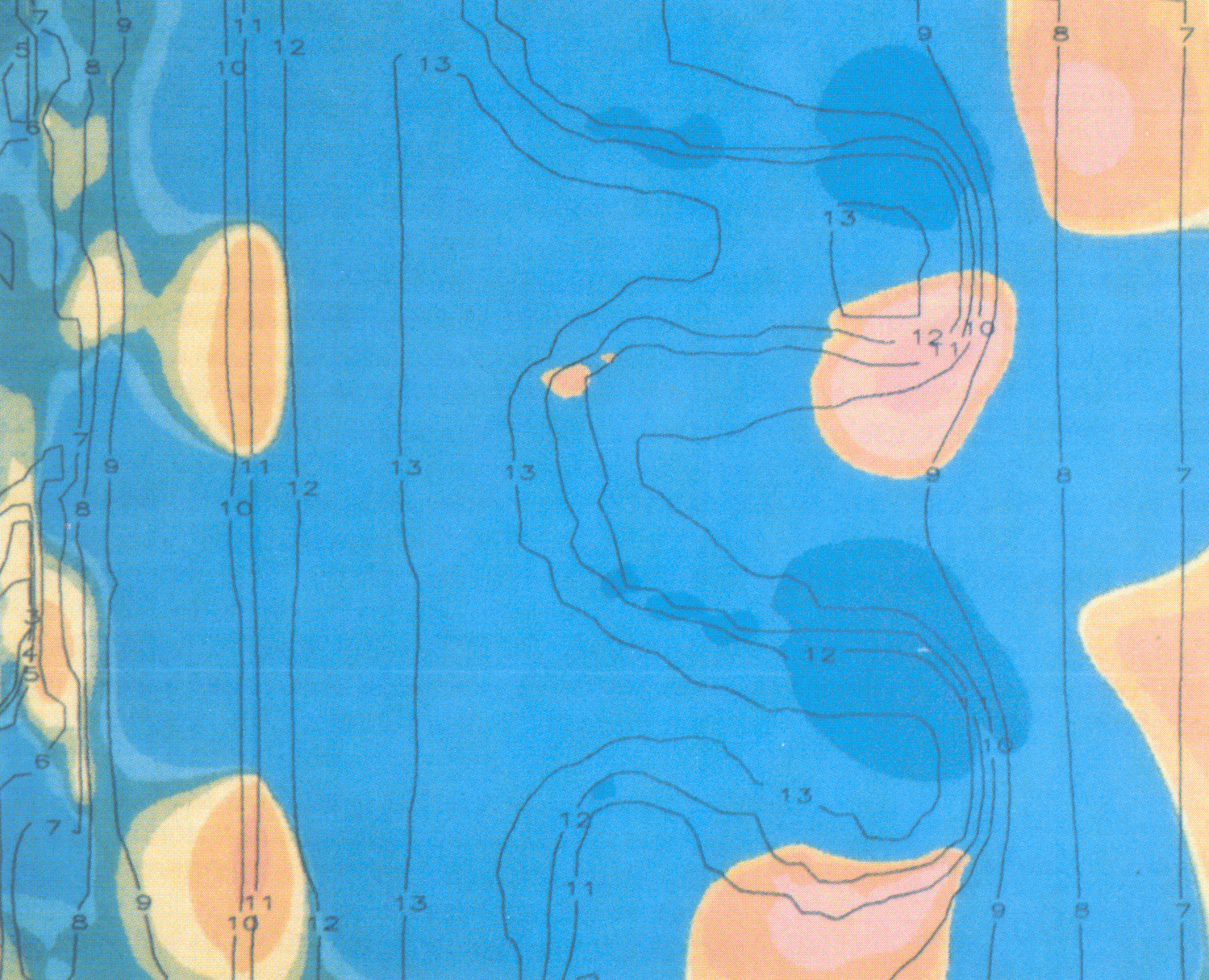
Laser Target Implosion Self-generated magnetic fields in laser irradiated targets have been modelled (Fig 5.2).

The reliability and performance of the machine have been exceptionally high and have led to a steady reduction in maintenance time. About 450 processor hours are delivered to users each week.
The Cray' operating system COS was brought up to version 1.16 and automatic migration of COS datasets to the Masstor M860 storage device was implemented, thus relieving some of the pressure on disk space. The Cray version of the UNIX operating system UNICOS was installed for system trials and is run once a week as a guest system under COS. User trials will start early next year when UNICOS 4.0 is implemented.
The scientific support organisation at RAL now has associated NERC and MRC as well as SERC staff covering the disciplines supported by SERC Boards and its remit is to foster the development of supercomputing techniques and applications in the broad range of disciplines using the Cray. There is also substantial contact with industry on collaborative schemes. Rolls Royce funded a fellowship at Pembroke College, Oxford, which includes collaboration with RAL staff on computational fluid dynamics topics.
As referred to above, an IBM 3090 mode1200E was installed replacing the IBM 3081K and Atlas 10. The new machine has 64 Mbyte of main memory, 128 Mbyte of expanded storage and a performance of about 35M instructions per second. It is a dual processor and has a vector facility attached to one of the central processing units. This is utilised by specifying an additional option on the Fortran compiler and gives considerably improved performance to many programs suitable for vectorisation.
The 3090 was installed at the end of March together with an extra 40 Gbyte of IBM 3380 disk space, and two extra IBM 3480 cartridge tape drives. These came into service on 6 April. One week later the IBM 3081 and Atlas 10 were decommissioned, as was 17 Gbyte of 3350 disk space.
Growth in the tape library has been confined to 3480 square tapes and almost 2500 are in use. The total of Masstor M860 cartridges allocated has not increased since last year but their disposition has shifted in favour of Cray-(241) and CMS (156) with a corresponding fall in MVS use to 198.
The customer Service Line continued its valuable contribution, handling 10,952 calls which resulted in 3258 incident reports (mainframes 1395, minis 402, terminals 550, and others for Pyramids, Suns, and Telecoms faults). 101 Alvey mail matters were handled.
Change Control processed 294 proposals of which 138 were handled by the new online system installed in June. Most changes were to mainframe software.
When the 3090 became operational at the beginning of April the VM extended architecture systems facility (VM/XA SF) was installed as a hyper visor to allow the MVS system from the Atlas 10 to run alongside the VMIHPO system from the 3081 which supported all the CMS and PROFS users. VM/XA SF allowed the 3090 expanded storage to be used efficiently for paging but did not have full support for CMS.
For performance reasons it was decided that the VM/HPO system should be removed as soon as possible which meant migrating CMS and PROFS users to run directly under the VM/XA system. The first step was taken in August when VM!XA SF was replaced by VM/XA System Product which has full support for CMS. Finally, the HPO system was removed in October but, to lessen the impact on users the same releases of CMS, PROFS and other program products were retained at the XA level.
The next stage, which has already begun, is to bring all these systems to levels which are fully supported under VM/XA SP and which can exploit the extended architecture 31-bit addressing. The extended architecture version of MVS has also been obtained for evaluation and a development system has been installed.
The introduction of VM/XA necessitated a major redesign of the support for line mode terminals accessing the mainframe via the network. This is now achieved by making use of the IBM virtual terminal access method (VTAM) instead of modifications to the operating system. A further move towards standard software will be the implementation of IBM products on the Amdahl 4705 communications controller to provide the interface to the JANET network.
A network response time monitor has been developed which runs on an IBM PC. This has a direct connection to the mainframe and also a connection via the network so that a measure of the difference in response from the two routes can be obtained.
The use of PROFS (IBM Professional Office System) continues to grow. There are now about 800 registered users and there appears to be no slowing of demand for connection to PROFS facilities. There has been a continuing programme of training new users throughout the year.
The pilot project to make the RAL PROFS system available to SERC Swindon Office, started in 1987, was concluded successfully in July 1988. Plans for the further expansion of PROFS at Swindon are being considered.
The dramatic increase in the use of the IBM relational database system SQL/DS reported last year has continued with a corresponding increase m the need for training and user support. The VM/CMS version of STATUS, developed by RAL under contract to Harwell Computer Power, has been marketed for almost a year. There is now a collaborative development on the new version of STATUS (STATUS/E) and a development project on interfacing STATUS to PROFS.
There has been an increase in the use of the RAL Financial Data System (FDS) by users and this has led to more demands for development. A staff-to-project system has been developed, demonstrated to a small number of users and is now being released to all RAL staff.
Progressively, the management information/decision support database systems developed at RAL are being made available through PROFS allowing a degree of integration of office and information services as seen by users.
A facility for improving access to and use of a database of information on SERC grants is being developed. This will be also be beneficial to an international project to link grants databases of several countries. This was reported last year as being a three-way collaboration between Italy, France and the UK. The Presidents of the Research Councils agreed at their meeting in Venice in May that this project should proceed with wider participation (eight countries) and RAL is actively involved in working towards that objective. It is possible that this system will be made available (with suitable security provision) to UK universities and science managers when it would provide a useful tool for establishing collaborations and for monitoring science progress.
There has been considerable development of scientific databases. Apart from regular advice and assistance to users on the use of database systems there has been continued development of the services of the World Data Centre for solar terrestrial physics and the Geophysical Data Facility - both located at RAL. There has been an increase in the use of the AMPTE database facilities and there appears to be a large and growing demand for further data sources from missions funded by APS Board to be made available.
The Laboratory supports the ISO standard GKS graphics system and has implemented the RAL-GKS version 1.11 which conforms to GKS 7.4, the full standard. GKS 1.11 is now installed on the IBM, Cray and VAX systems. With this new release, most known deficiencies in the previous (0.11) release have been removed and many handlers added supporting modern devices. Work continues on the development of further handlers for VAXStations and X-Windows. Many bottlenecks in the service, particularly in the size of files which can be routed to central hard-copy devices (such as the Versatec 42" colour plotter, Fig 5.3) have been eliminated in the latest release.
SERC has joined with the other Research Councils and the Computer Board in the purchase of the UNIRAS collection of graphics packages and utilities. As a result, UNIRAS may be installed on all computers in UK higher education environment. It provides a comprehensive set of higher level graphics tools for the presentation of results pictorially with callable packages for use by programmers and interactive utilities for non-programmers.
A viewing system has been developed for the IRIS 3130 workstation which permits the rapid viewing of results produced by the Cray. This system accepts computer graphics metafiles (CGMs - ISO standard 8632).
During the year, all equipment in the Cray video facility has been tested and software developed to allow the interpretation of Computer Graphics Metafiles. A pilot video has been made from computational fluid dynamics results. The system is now being enhanced to the level of a production service and is due for release in January 1989. This facility will allow users to direct existing graphical output to video tape (U-Matic or VHS), with control over the correspondence between their original pictures and frames on the video tape. ThIS wIll allow either a pseudo-slideshow effect (with cuts or fades between pictures) or full animation.
The expansion of the fibre optic ethernet LAN backbone has continued at RAL and there are now 9 villages connected and over 100 computers or workstations attached. Two new lines have been ordered to provide links from RAL to European sites. The first is a 64 kbaud (kilostream) line for the EARN link from RAL to CERN to replace the existing 9.6 kbaud.line. The second is a 19.2 kbaud analogue private wire from RAL to the Joint Research Councils office in Brussels.
Communications between research workers in the UK and the US will be significantly enhanced by the provision of a direct link between the high performance backbone networks in the two countries, JANET and NSFnet. This project was initiated by the National Networking Unit and is jointly funded by the National Science Foundation in the US and the Computer Board, SERC and DTI in the UK. The link will be via the new TAT8 transatlantic optical fibre and the initial services supported will be electronic mail, file transfer and interactive terminal access via a new gateway in London. The new gateway started service in June using an interim transatlantic link. The new link is expected to be available early in 1989.
On the European front, the specification phase for the COSINE project was completed in the summer. This project aims to establish a pan-European network infrastructure for the research community based on ISO standards. The project is supported by the European Commission and many European countries. The implementation phase is scheduled to start in January 1989 and includes the provision of an X.25 network to interconnect the national research networks and improved networking facilities between the US and Europe. The UK academic community and the National Networking Unit are major participants in this project.