

The Annual Report covers the year ending September 1987. Its main purpose is for internal use in the Division, indicating what has been achieved and by whom. Hopefully it also gives new members of the Division some idea of the work programme and its objectives.
The main responsibility of Informatics Division is to support SERC' s Engineering Board's activities in the information systems and CAD areas. This splits into two main areas:
Computing Facilities Committee: CFC provides an infrastructure support to the various Engineering Board subject committees. Applications software of interest to more than one committee is supported centrally. The Committee is establishing an Engineering Applications Support Environment (EASE) which provides support from the application level down to the hardware that it runs on.
A recent initiative has been to provide support for transputer related activities in the university and industrial environment.
Alvey: The Alvey Programme started in 1983 and was aimed at providing a significant impetus to cooperative, pre-competitive research in the enabling and underlying technologies of Information Technology. The Division has been responsible for the development of a hardware and software infrastructure for the IKBS, SE, and MMI areas. This started in 1984 providing multi-user system support via a distributed set of GEC Series 63 and SYSTIME VAX systems. More recently support has also been provided for SUN systems.
The Division also provides coordination and support in the areas of IKBS, MMI and SE.
A third major interest in the Division is:
The Division's aim is to keep a good balance between the research, development and support activities believing that omitting anyone area weakens the overall quality of the Division's expertise.
The internal organisation of the Division has changed significantly during the year. At the start, the Division comprised three Groups:
The Applications activities of CFC were part of Technology Division, as was the support for the Image Processing and Speech/Vision part of the Alvey MMI activities.
During the year, a number of major changes have taken place which has meant several reorganisations. It is hoped that the instability of the current year will not be repeated in future years. The major changes have been:

The loss of two senior members of the Division in a period when the Division expanded significantly in size has put a severe pressure on the organisation of the Division. A Staff Review is in progress to ascertain the number of senior posts necessary to run the Division. The current interim Group structure is:
Organograms showing the Divisional structure at the start and end of the year are given as Appendix A.
Due to several changes in structure during the year (some quite recent), it has been difficult to provide a report that closely matches the Group structure. The main sections are as follows:
Due to the recent arrival of the Image Processing Section, their activities are not reported in this Annual Report.
The main activities in the Software Engineering area are:
Management, Technical Support and Development work are funded directly from Millbank to SERC/RAL. The research work is funded differently. This either follows normal Alvey rules, or goes through the peer review system of IEC/CSSC. At any instant the aim is to have more than one project underway with successors in the pipeline. SKE aims to have both Alvey and CSSC funding simultaneously. It is hoped that funding via ESPRIT can also be obtained.
The Division has continued to provide management support to the Alvey Programme. Since the major part of the programme is now in place attention has concentrated on monitoring the individual projects and installing a procedure for disseminating the information generated by the programme.
An increasingly important aspect of the overall support as the programme develops is the analysis of the budget and preparation of data for forward planning. For this purpose a special procedure has been developed with the objective of minimising difficulties associated with over commitments of the budget.
Now that the results of the programme are becoming available, attention is turning to plans for exploitation of these results. All industrial and academic participants in the SE programme have been asked to provide the Directorate with their outline plans for possible exploitation of their products generated under the Alvey programme.
Attention is also being fixed on the evaluation of the programme and this end information is being gathered arising from the dissemination of information programme.
F M Russell, J M Cheney and T Mawby supported by Lillian Valentine, undertake the above work.
The section undertakes specialist infrastructure work for the Alvey SE programme. The way of working that seems most satisfactory is for the section to work alongside a specific Alvey project to provide a piece of infrastructure needed by that project, but to do so in such a way that it will be of use to the whole community. An example of this is the project to provide a yacc-1ike tool for Standard ML.
ML is a functional programming language which was designed and first implemented at Edinburgh as the metalanguage for the interactive theorem proving system LCF. ML soon attracted interest quite independently of LCF with the result that a number of dialects appeared.
Standard ML (SML) is a consolidation of tried-and-trusted developments which has been agreed by the ML community.
Mikael Hedlund (PMH) worked on converting the old ML/LCF system to SML under the guidance of Chris Wadsworth (CPW). The SML implementation was completed in June 1986. During this year the LCF source files written in old ML were transliterated to SML and the new system was tested. Larry Paulson at Cambridge University kindly assisted with evaluation of the new system and suggested some changes to the system to make the object language (PPLAMBDA) more consistent with SML (the metalanguage). These changes have now been completed. A code optimizer was also built which improved the performance by a factor of 10. The work has been documented and the Rutherford SML/Cambridge LCF System is now ready for distribution to interested researchers. Brian Matthews (BMM) is handling distribution of the system.
Valuable feedback was also obtained from Anthony Clair at East Anglia who ran his benchmark programs through the compiler.
The old LCF system (still being used by Cambridge) and the Edinburgh SML compiler were mounted on UTS in collaboration with Stanley Ooi in Infrastructure Group.
The aim of this project is to produce a yacc-like parser generator written in SML which produces output code in SML. This project is being undertaken on behalf of the Alvey FORSITE project.
FORSITE is a collaboration project between the University of Oxford, Racal ITD Ltd, the University of Surrey and System Designers Plc. The FORSITE project is producing an environment to support the development of formal specifications in the Z and CSP notations. Both are products of Oxford's Programming Research Group. At the present time the main components of the environment are a multi-font WYSIWYG editor for mathematical texts and a type checker. The latter is written in SML. Current research in FORSITE is concerned with a proof checker for Z.
SML/yacc system is needed by FORSITE to provide a Z parser that will integrate neatly with the other components of the environment.
A specification for SML/yacc system was drawn up by PMH and BMM, and has been approved by FORSITE. The system has been designed for general use and not just to meet the requirements of FORSITE and is consequently very flexible.
Coding and testing are now well in hand.
In February 1987, the Laboratory for the Foundations of Computer Science at Edinburgh asked if the Division would collaborate with them in developing graphical user interfaces for software tools being constructed.
Edinburgh are developing a number of tools for supporting formal software development methods that would benefit greatly from graphical user interfaces. One such tool, the Concurrency Workbench, seemed particularly appropriate for a pilot study. The Concurrency Workbench is a suite of tools for manipulating and ana1ysing concurrent systems described in their CCS (Calculus for Communicating Systems) notation. The first prototype, with a simple textual interface, is now completed, and the aim of the collaboration work is to develop a graphical user interface for these tools. The tools are written in SML and the project will be organised in such a way as to produce a general purpose user interface toolkit for SML.
HCI section of the Infrastructure Group will be providing the people for the project, funding comes from the Alvey Software Engineering programme.
Theorem provers are software tools to aid in the process of proving theorems. In the software engineering context we are primarily concerned with theorems about programs, for example that a particular program has a particular property.
Beside the LCF system mentioned above, the group has continued its involvement with the Boyer-Moore theorem prover from the University of Texas. We have not been working with the Boyer-Moore system ourselves but have continued to act as a UK distribution point for the Alvey SE infrastructure.
The overall software engineering research theme is Quality Certification of Software Products. Within this theme, the main research interests of the group are in formal specification, the development and application of machine-assisted proof systems and the role of formal reasoning in software development.
In September 1986 David Duce (DAD) held two research grants, one from the Alvey Software Engineering Programme entitled Specification of the Graphical Kernel System (GKS), the second from SERC's Computing Science SUS Committee entitled Theoretical Studies of Emerging Computer Graphics Standards.
The Alvey grant terminated in March 1987 and a Final Report was duly submitted to the Alvey Directorate.
The main thrust of the technical work during 1986/7 was to produce a reasonably complete specification of the output side of GKS. The major piece of work during the year was to devise what seems to be a general framework for the GKS output specification. Dr David Arnold and Graham Reynolds at the University of East Anglia have an SERC funded project on configurable models of graphics systems. Graphics processing pipelines provide a convenient conceptual model for many graphics systems and the UEA project is exploring this idea further by trying to identify general classes of processes and connectivity in such models. In November 1986 DAD was invited to spend a week at UEA trying to give formal specification of these models. It turned out that this could be done very neatly in the Z specification language using partial functions to model primitives, Z schemas to define the operations in the pipeline and the schema piping combinator to describe the composition of operations in a pipeline. This scheme is described in a joint paper accepted for the Eurographics 87 conference. This work has been applied with very encouraging results to the specification of GKS. Michael Parsons (MSP) has worked on this and a draft paper has been produced which describes the polyline, polymarker and fill area primitives in this framework. There are some difficulties fitting GKS into the framework, but we are of the opinion that these are due to inherent problems in GKS. These views have been recorded in a position paper submitted to the Eurographics GKS Review Workshop to be held in September 1987.
In November 1986, the PHIGS review provided the opportunity to look again at the GKS input model. The led to proposals made jointly with Bob Hopgood for extensions to the PHIGS input functions to allow multiple logical input values to be returned from a single trigger firing in REQUEST mode. A simple example of the need for this facility is the cross hair cursor input on Tektronix devices, where a single key press returns the position of the cursor and the identity of the key hit. The obvious mapping of this onto GKS is to a pair of logical input devices, a LOCATOR for the cursor position and CHOICE for the key hit.
In subsequent discussions with Clive Ruggles and Yee of the University of Leicester, a formal specification of the GKS input queue was developed which fits nicely with this model, and from the insights gained in this exercise a paper was written containing a range of proposals for extensions to the input model. This is about to appear as an RAL report. The proposals were refined further in discussions with Robin Langridge of the CAD Centre and Graham Reynolds, and were submitted as a UK Experts paper to the PHIGS review in May 1987. The proposals have also been submitted to the GKS Review Workshop.
DAD also wrote review papers on formal specification of graphics software for the CIL 87 Conference (invited paper) and the NATO ASI on Theoretical Foundations of Computer Graphics and CAD (invited contribution).
Progress on the second project concerned with PRIGS and GKS-3D has been slower. The work on extending GKS to enable PRIGS to be defined on top of GKS, reported in the last Annual Report was taken further in the light of the discussion of those ideas at the PHIGS review in September 1986. Work started on proving properties of the extensions using Jeremy Dick's ERIL system, but this work is yet to be completed. We have also had some preliminary thoughts on how to accommodate GKS-3D and PHIGS in the specification structure described above for GKS and to work this out in detail will be the subject of the next year's work.
Following the PHIGS review meeting in May 1987, a short paper has been written which analyses the PHIGS nameset concept and shows that it is, in some sense, a bad thing. These results are influencing the functionality to be provided in the Incremental Spatial Search capability recently incorporated into PHIGS.
DAD and MSP both participated in the BSI Computer Graphics Panel and in the PHIGS international review. DAD retired as secretary of the BSI Panel in November 1986, but did not escape the call of duty, being appointed secretary of the PHIGS meeting in May 1987!
Jeremy Dick's (AJJD) research continues in the field of Automated Equational Reasoning. The ability to reason with equations (for example, to deduce conclusions from a set of equations), is important in a number of areas, for example specification of abstract data types and their validation, program transformation, synthesis of programs, program optimisation and solving equations.
AJJD has over a number of years developed a rich theoretical framework for equational reasoning and has developed a practical tool, ERIL (Equational Reasoning an Interactive Laboratory) based on this framework. ERIL is a useful tool for experimenting with the specification and prototyping of abstract datatypes, and is used by several research groups in the UK and abroad.
ERIL is based on the use of rewrite rules for computing and reasoning with equations. One of the potential applications of this approach is to theorem proving, and the aim of the present research is to compare the scope and performance of a theorem prover for a particular logical system (polymorphic predicate calculus) with traditional approaches, and assess the long- term potential of this new approach to theorem proving.
There are two main thrusts to the present stage of the project:
John Kalmus (JRK) joined the project in January 1987 and the combination of AJJD's computer science and JRK's Mathematics background is proving very useful.
A new variant of the Knuth-Bendix algorithm by Jieh Hsiang (Stony Brook, New York) was implemented in ERIL. This version overcomes some of the cases where the original algorithm fails because an axiom cannot be oriented into a rule. Initial experiments suggested that Hsiang's method is not really satisfactory for handling permutative axioms, and it is necessary to proceed with the implementation of an association - commutative unification algorithm.
A fruitful collaboration has developed with Dr Ursula Martin of the University of Manchester (soon to move to Royal Holloway and Bedford New College). A draft of her paper for the Second International Conference on Rewriting Techniques and Applications on a new means of orienting rewrite rules was studied and her ideas were expanded sufficiently for an implementation in ERIL. This work will form the basis of a full research paper, jointly authored with Ursula.
Discussions held at the First Workshop on Unification will help towards the achievement of the second goal, the extension of unification in ERIL from the empty equational theory (standard Robinson) to arbitrary equational theories.
AJJD is also working on a technical report on data structures for the representation of rewrite rules. Current progress warrants considerable optimism for another paper by the end of the year. The ERIL system was used by Professor Bertran-Salvans, a Visiting Scientist from the Polytechnical University of Catalonya in Spain, for studying a model and semantics for a notation for parallel computation. It extends the familiar context-free grammar notation for the definition of a type of two dimensional strings, to model parallel and sequential execution. In addition, grammar rules are parametric. ERIL has been used to experiment with a set of transformation laws and a normal form for expressions in the notation. The results are described in an RAL report.
IPSE 2.5 is a major Alvey project to research and develop an Integrated Project Support Environment based on advanced distributed systems and man-machine interfaces, and incorporating support for both the practice and organisation of design tasks. A major objective is the development of an integrated framework for supporting the use of formal methods in software development, including formal specification and theorem-proving techniques.
The project began in October 1985 with three initial collaborators (ICL, STC and Manchester University) and had a successful first review with the Alvey Software Engineering Directorate in July 1986. RAL applied to join the project from April 1986 and, after some delay, received its grant allocation at the beginning of July 1986. Three additional industrial partners have also recently joined the collaboration.
At RAL, Juan Bicarregui (JB) and Brian Ritchie (BR) are now engaged in the project. Chris Wadsworth managed the project until joining the Transputer Initiative in January 1987. DAD is now the RAL representative on the Project Review Board.
The work at RAL is carried out in very close collaboration with the University of Manchester. JB and BR spend a fair proportion of their time at Manchester.
At the start of the year a lot of time was spent in familiarisation with the project and formal techniques in general. BR wrote a review of his Interactive Proof Editor (developed at Edinburgh) for inclusion in the IPSE 2.5 Deliverable, Theorem Proving Review paper.
The Manchester/RAL part of the IPSE 2.5 project is concerned with the support of formal methods of software development and in particular with aiding formal reasoning itself. The intention is to build tools which enable a user to construct proofs at the workstation; modern workstations such as the SUN3 should make it possible to design proof assistants which are much more usable than earlier tools developed around 'glass teletype' interfaces.
Initial work was concerned with generating a scenario of usage for a hypothetical system supporting construction and refinements of VDM specifications, and extracting requirements from this for a "VDM store" (database) of specifications and proofs.
BR and JB have also commented on the specification of Muffin, a prototype interactive theorem proving system being built at Manchester as a test bed for ideas.
BR used SML to build a rapid prototype of a part of the Muffin prototype formal reasoning tool. Tests on this revealed a flaw in the initial Muffin specification. This has now been superseded by the subsequent complete implementation of Muffin in Smalltalk-80 at Manchester.
One of the major problems being tackled by this part of the project is how to build a formal reasoning tool in which the logic with which the tool operates is in some sense a parameter. The idea is to have a very general tool which can be instantiated to produce a tool for reasoning in a particular logic, say predicate calculus or temporal logic (a bit like a compiler-compiler). JB is working with Peter Lindsay from Manchester on the theoretical underpinnings of this idea.
BR is working on specification language instantiation with Cliff Jones at Manchester and with JB on theory stores. In the latter area BR has been working chiefly towards the production of a requirements document by generating scenarios of specification development in several languages (primarily LARCH and VDM) and attempting to draw general results from these. This document is due to be reviewed by the project at the end of August 1987.
Tony Cox (ADBC) has spent almost all his time working on the Alvey (VLSI/CAD) funded research project The Transformation and Verification of Occam Programs, which is a collaboration between Inmos Ltd and Oxford University; at Oxford the project has consisted of Dr Bill Roscoe, supervising, and two research officers, in addition to ADBC.
A prototype system has been written in Edinburgh Standard ML which is able to parse Occam Programs, apply any of the transformation laws and to convert a program to normal form, including infinitary programs to a specified number of communication steps. ADBC has done almost all the programming on the project, while other members have contributed ideas on concurrency theory and the user-interface.
The basic ideas of implementing transformation rules as SML functions are being reviewed. The inspiration for this came from a paper by Larry Paulson (Cambridge) on his Isabelle system for constructive type theory, where inference rules rather than theorems are the central data type. The idea is that derived rules should be more efficient with this approach, but it is not yet clear how readily this applies to the Occam transformation system.
The prototype transformation system was used in earnest in the development of the floating point transputer and proved to be of real value in the development of a very complex system.
ADBC has remained a member of the BSI working group producing a Prolog Standard, taking an active interest in the Semantics sub-group.
We were honoured to have Prof Miquel Bertran-Salvans from UPC, Barcelona as a visiting researcher from March 1986 to March 1987. MBS has been interested in Dimensional Design, a graphical technique for presenting software designs originated by R W Witty (RYW) and DAD for use in the FR80 Driver and Roots toolset.
A collaborative project between members of the section (MBS, Duncan R Gibson (DRG) , RYW) and DEC(UK) (Tom Povey) was established to build a syntax-driven compiler/compiler/editor system to be called the Dimensional Design Editor (DDE).
A requirement specification, user interface prototype and initial design work had been completed by July 86 when DEC posted Tom Povey to the USA and thus had to withdraw from the collaboration.
By the time the project terminated in March 87 the kernel of a generator of DD syntax-driver editors had been completed. This comprises a set of Pascal functions and procedures.
Grammars for the definition of Dimensional languages can be input to the kernel in order to obtain syntax-driven editors for different languages. An editor for a simple Pascal type language was developed. Grammars can be edited with the syntax-driven editor itself.
The kernel is described in an RAL report. Coding the system required a large amount of work by DRG.
We are honoured to have Mario Martins (MM) from the University of Minho, Portugal as a Visiting Scientist from March 87 to December 87.
Text editors are the most widely used software components of any interactive computing system and in the last few years a new generation of editors has emerged based on sophisticated interactive techniques. Spy is a prime example of such an editor. Formal specification of text editors has received very little attention, given the number of text editors in use.
MM has been developing a specification of Spy in Oxford's Z specification notation. To increase the modularity and readability of the specification the editor was divided into four subsystems, the Editing System, the File System Interface, the Display Control System and the Window System. The schema notation in Z allows complex specifications to be presented in manageable chunks and this facility is used to great advantage in this specification. The editor specification is developed in easy stages, corresponding to increasing richness of functionality. The specification starts to get difficult when the UNDO facility is introduced. One suspects this is an experience shared with the implementation!
A report describing the specification has been produced, but has not yet been circulated.
Brian Matthews was welcomed to the SE Section in September 1986 and Juan Bicarregui in October 1987; John Kalmus and Michael Parsons in January 1987. Terry Mawby was welcomed to the Alvey SE Management Section in June 1987.
Chris Wadsworth moved to EC Group in January 1987 to play a leading role in setting up the Transputer Initiative. Duncan Gibson transferred to EC Group in April 1987 to work on text processing.
Professor Miquel Bertran-Sa1vans returned to his university in Spain at the end of February 1987. Mario Martins, a Visiting Scientist from the University of Minho in Portugal joined us in March 1987. Professor Lockwood Morris is a Visiting Scientist on the IPSE 2.5 project from July 1987 for nine months.
Mikael Hedlund left us in June 1987 to return to his native Sweden.
Dr Stuart Robinson, a Visiting Senior Lecturer from Brunel University joined the group in April 1987. He spends one day per week at RAL. His initial work at RAL is transputer related and is described elsewhere in this report. He is also advising BMM on the yacc-SML project.
Funding wise the year has been a time of relative stability and it is hoped this situation will continue for the next year. Our aim now is to produce good quality research and strengthen our links with other research groups in academia and industry both nationally and internationally. We hope to be able to set up joint projects with some of the Institutions we are now working with informally. We will also be looking carefully at ESPRIT II as a possible source of future funding.
| SEG Number
145 |
IPSE 2.5 Note 4 - Visit Report Tim Griffin, Edinburgh | B Ritchie | 02.09.86 |
| 151 | Trip to USA | R W Witty | 27.10.86 |
| 154 | The Incorporation of Standard ML in the Cambridge LCF System | P M Hedlund | 27.11.86 |
| 156 | Trip Report USA 6-22.12.86 | P M Hedlund | 09.01.87 |
| 157 | Edinburgh Standard ML | P M Hedlund | 13.02.87 |
| 159 | SML-Yacc A Compiler-Compiler in Standard ML | P M Hedlund | 18.03.87 |
| 160 | Trip Report - Barcelona 17-25.3.87 | D A Duce | 01.04.87 |
| 161 | The Incorporation of Standard ML in the Cambridge LCF System | P M Hedlund | 27.05.87 |
| 162 | Trip Report - NATO Study Institute 11 Ciocco, Italy, 4-17 July 1987 | D A Duce | 20.07.87 |
| 164 | Trip Report - NATO Study Institute 11 Ciocco, Italy, 4-17 July 1987 | M S Parsons | 20.07.87 |
M Martins, Formal Specification of Highly Interactive text Editors - The SPY example, June 1987.
DAD
MSP
AJJD
JRK
BR and JB
PMH
BMM
BMM is taking an MSc Course at Imperial College London in the Foundations of Advanced Information Technology (FAIT). This is on a part time basis, two days a week for two years. This course is intellectually very demanding, but gives a very good foundation in theoretical computer science. BMM is now engaged in a group project with other part time students. The project involves the implementation of optimisations to Prolog programs using Abstract Interpretation of of those programs. This is based on work by Jones and Sondergaard, Mellish and others into the abstract semantics of Prolog and alternative interpretations of those semantics to find significant properties whilst ignoring other attributes irrelevant to the analysis in hand. It is hoped to optimise Prolog for such things as groundness analysis, circulatory analysis, and help in solving the occur check problem.
DRG acted as secretary to the Alvey SE Staff Meeting from January until June 1987, and as the section's representative to USM until June 1987.
AJJD is secretary to the Alvey SE Formal Methods Advisory Group. He has been secretary since January 1987.
DAD assisted William Newman of the Alvey Directorate in organising a meeting on Formal Specification and Graphics, held at RAL on 12 June 1987.
DAD continues as Vice Chairman of Eurographics, participates in the Executive and Professional Board activities and is Programme Chairman for the Eurographics 88 event in Nice.
DAD produced the camera ready copy for a volume in the Eurographics Seminars series (Springer-Verlag) entitled GKS Theory and Practice. This is a collection of published papers on GKS which should be of particular interest to anyone implementing GKS. DAD is now editing a book on Knowledge Representation with Gordon Ringland, which contains contributions from many members of the Division.
There were four recruits during the year and one loss.
Sandwich students

Helen Jenkins was secretary other than for a period of sick leave when Jacqui Smith substituted. During September 1987, Jacqui Smith had an exchange for one month with Liu Catena of Italy.
Knowledge Engineering section has the following objectives.
The support effort is going very well and helped to preserve continuity over the change in IKBS Director at the beginning of the period. In some areas - monitoring, research clubs and SIGs, software support, and mailshot - the work has grown considerably with the maturity of the Alvey programme. New initiatives now successful have included the launching of the Logic Programming club, the AI facility for the Environment committee (termed ARTIFACE in subsequent sections), organisation of the IKBS/Architecture exhibition and various meetings at the Alvey conference, contribution to and organising the production of the IKBS strategy for IT92, collection of abstracts for IKBS and architecture projects and organising a Knowledge Acquisition workshop on behalf of the Computing Facilities Committee. Some time has also been spent in discussions about LOOKALIVE, a potential post Alvey project in Health.
On the R&D side, PARALFEX (GAR), a funded Alvey Project, has produced some impressive demonstrations and application has been made for a year's extension. DFM obtained SERC support for the 'Intelligent Front End' project and preparation of a proposal for an Energy Kernel System is well advanced. There is now a large amount of software implementing Conceptual Structures and a paper (MKJ) has been accepted for ES87. Various initiatives are giving the group a technical visibility, including a shortly to be published book on Knowledge Representation (Eds DAD and GAR) numerous external talks and book reviews by members of the group, and organisation of a workshop on KR (GAR, DMR) attended by prominent international figures.
There has been little effort left for much activity in in-house applications; the major task has been the attempt to build an expert system in ion-source conditioning for ISIS. It is hoped that a RAL report on expert system shells shortly to be produced (MBD) will help to promote this technology in the laboratory.
As the Alvey programme matures, the emphasis has switched towards assessing the achievements of projects and publicising them. The balance of work in the support area has thus slowly changed, although the total seems to continually increase, given major events like the Alvey conference. MBD has continued to act as Secretary to the monthly meetings held to ensure that the disparate parts of the Alvey organisation (RAL, Swindon and Millbank) continue to move in step. CJP attends the Alvey IKBS and Architectures Advisory group and the Alvey Infrastructure committee. AJL is secretary of SIGAI.
A two day meeting of the KBS Club (secretary JYS) was organised in January at St Anne's College, Oxford. The format was a combination of reports and tutorials. There were many positive comments from the 56 attendees on the meeting, especially for the quality of the tutorials. The sessions on Deep Knowledge were led by Ken Forbus from the USA. Selected papers from this meeting were distributed in the May issue of the IKBS Mailshot. There was a one day open meeting of the Club at the Alvey Conference. This included nine presentations on the the theme Results - what has been learned. There were over 70 participants. A report on the session will appear in the Conference Supplement to the September edition of Alvey News. St Anne's has been booked for the next two day meeting planned for 11/12 January 1988. The KBS Club steering committee has met twice.
During the period, the Architecture Club (Secretary MBD) has begun to take a more active role in providing a focus for the Systems Architecture projects. In November 1986, the Club held a meeting on benchmarking new architectures; some progress was made in beginning to establish a suite of benchmarks. In March 1987 the Club held a meeting on exploiting parallel machines. A useful exchange of views was held; in particular, experience on Esprit and other projects proved a very valuable input. The activities of the Club has continued to be controlled by a Steering Committee (Secretary MBD). The Steering Committee has been responsible for establishing Special Interest Groups covering Knowledge Manipulation Engines and Systems Architecture on Silicon (jointly with the High Performance Silicon Structures Club); these SIGs have been very active. A SIG is also being established on Parallel Declarative Systems, and a meeting has been supported on Persistent Information Architectures.
The Logic Programming Club (secretary BGB) has had two technical meetings, organised with the help of Steve Torrance (Middlesex Poly) who was appointed as Logic Programming coordinator at the beginning of the year. A workshop is now being planned to consider the future directions for logic programming. An occasional Logic Programming mailshot has been sent.
The workshops supported by Alvey in IKBS and Architecture have been a highly successful part of the whole programme, bringing together academics and industrialists (often with a foreign visitor) to discuss specific topics in some detail. About 15 such workshops have been supported over the last year. MBD (and SGD) are responsible for ensuring that proposals to hold workshops are properly vetted and form part of a coherent programme and for overseeing the administrative arrangements.
MBD is responsible for appointing and overseeing the work of Monitoring Officers (and uncles) to the projects. Apart from occasional changes, the MOs are now fully in place and the emphasis has switched to obtaining feedback from the MOs on, for example, technical progress, exploitability, milestones, etc. This may well have put a greater load on some of the MOs than they had anticipated.
Members of the group personally monitor certain projects in the infrastructure and Vision areas as well as three Alvey community clubs RICS, WIESC and TRACE. GAR was a member of the ALFEX Steering committee for most of the period.
Arrangements have been made (MBD and SGD) for collecting abstracts of reports produced on IKBS and Architecture projects and publicising them as a supplement to Alvey News. About 100 abstracts have already been received and a selection of them should be published shortly.
The AI/IKBS Community is supported through the provision of software by the group; through the provision of support by University groups under contract to RAL; and through the commercial provision of software. Information on this can be found in our publication AI Software available on Alvey Infrastructure Computers now in its seventh edition.
The Special Interest Group in AI was established by the SERC to advise the Alvey IKBS Director and SERC Boards that support AI on the software, hardware and standardisation needs of the research/R&D community and the projects that might someday enhance the UK AI industry. I t is comprised of Industrial and Academic suppliers, developers and users of AI products. RAL organises the group, provides an interface between SIGAI and the groups it advises and, where appropriate, places contracts or encourages applications for research grants to implement its recommendations. The contracts so placed are monitored by this group for SIGAI.
The contracts include those that provide for the support and development of NIP (at Edinburgh AIAI) and POPLOG (at Sussex and SD). They also provide support for Lisp users (from Edinburgh AIAI); and for some of the UK effort on the international committees developing standards for Prolog and Lisp. They have enabled the Prolog and Lisp libraries at Edinburgh to be made available to users over the electronic networks.
The New Implementation of Edinburgh Prolog (NIP) is distributed by this group to SERC and Alvey supported groups for research, teaching and evaluation free of charge. We are currently distributing a new version (1.5) that has an enhanced user interface for the Sun Workstation and an interface to the editor "GNU Emacs" which is distributed with it. There are 57 groups using NIP.
The continuing development of NIP is supported by a contract which is administered by this group with advice from SIGAI.
The development environment, POPLOG, which includes the main AI languages of Lisp, Prolog and POP is being developed by the University of Sussex and Systems Designers under a contract administered by this group with advice from SIGAI (see below). The systems is being supplied, with support, by Systems Designers to 29 Alvey funded groups under a contract placed and administered by this group. The upgrading of the Lisp system to Common Lisp has just been completed and the final full implementation will shortly be available commercially.
A SIGAI contract helped to initiate the Knowledge Representation System Trials Laboratory at Edinburgh AI Applications Institute this enable academic and industrial researchers to gain access to advanced Knowledge Representation toolkits. CJP and a DTI representative jointly monitor this and a related facility the Parallel Architectures Laboratory.
As the result of a recommendation from SIGAI, Imperial Software Technology (IST) was commissioned to produce a new suite of benchmarking programs for Prolog systems. As part of this development, existing suites were subjected to analysis by a group at Cambridge. The new suite, known as the "Alvey Prolog Benchmarks", has been used on a number of different systems by this group and the results subjected to the same analysis by the Cambridge group - with some very interesting results. The suite, the original report from IST, our results and a report on them, together with the report on the analysis of those results by the group at Cambridge, are available.
CYLK continued to serve on the BSI PROLOG Standardisation working group.
The Mailshot has grown steadily over the past year, both in size (from 20 items per mailing to nearly 40 per mailing) and in the number of recipients (from 400 to 480). The Mailshot has become well known in the AI community and is now an accepted place for advertising research vacancies and academic meetings of all kinds.
The Bulletin Board was re-launched at the beginning of February. It has grown rapidly and there is now an issue approximately every two weeks. Like the Mailshot it has gained a reputation as a good place to advertise research vacancies and to announce meetings. At present there are nearly 150 JANET addresses in the mailing list, some of these auto-mailboxes representing University research groups rather than individuals. In addition there are the USENET recipients but it is very difficult to estimate these. They could exceed the number of JANET readers.
The Catalogue of AI Techniques (formerly called the Catalogue of AI Tools) continues to be maintained in book and database form. References to commercial shells, etc, have been removed and the amount of detailed information on genuine techniques has been increased. The updated version of the database (based on the 3rd as yet unpublished edition of the Catalogue) is now available in database input form. A small amount of editing is still required before it can be installed.
JWS acted as secretary of this group, set up by the IKBS Directorate following initiatives from the KBS Club and SIGAI. As a result, two short-term proposals received Alvey funding. After many meetings, including a two day session at Milton Hill House, a draft report covering long term recommendations has been produced.
There is still some work in allocating SUN equipment although it has reduced a lot. The group still administers a pool of Whitechapel computers and also the ICL Series 39 systems in the Architecture programme. There are preparations to replace one of these by a larger machine to meet the requirements of the Software Engineering IPSE 2.5 project.
The group were involved in organisation of this. CJP was responsible for the IKBS/Architectures exhibition; this meant planning the layout, organising the exhibitors, loaning SUNs, organising photographers etc. (Tony Rush from Scientific Admin gave invaluable help). JWS organised the KBS club session and BGB the Logic programming club. They both were official rapporteurs as was also CKYL in an Architecture session. CKYL was also responsible for configuring the SUNs loaned from RAL.

The IKBS Advisory Group asked Professor D Sleeman to prepare IKBS Strategy Recommendations for IT92. CJP contributed the infrastructure sections, took responsibility for production and did a small amount of editing. Both the main strategy document and a substantial Annex are produced and distributed to the community.
The SERC's Environment Committee, as part of an awareness program, has funded an AI Artificial Intelligence Facility for Engineers. This includes a Sun 3 160M-4 workstation, and two IBM PCs equipped with AI software and tools by this group. They are loaned to Engineers in Universities for short periods for evaluation.
There was a substantial evaluation of LISP machines to run KEE (performed with the assistance of Edinburgh University AIAI), but the recommendation to buy Xerox was never followed up as the Committee concerned ran out of funds.
A workshop on Knowledge Acquisition was organised at Cosener's on behalf of the Computing Facilities Committee who wished to educate members of EB committees. The proceedings have been edited and will be distributed to every member of EB committees. MDW organised and spoke at the workshop, CJP helped with the editing, GAR, JWS, SCL assisted with note taking. HJ was conference secretary.
RAL was asked to assist with preparations for a possible Applications project in Health in a post Alvey programme. Meetings were organised at RAL with ICL and the project coordinator from the NHS; MDW was secretary.
Work has continued on this Alvey funded project to investigate knowledge representation strategies in the financial sector.
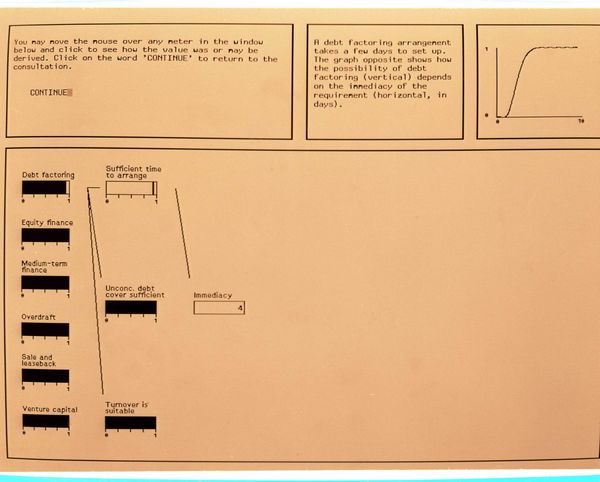
The Knowledge Base used is based on data provided by the Alvey finance community club ALFEX for their Source of Finance Advisor (SOFA). The project initially implemented this on an IBM PC in the shell Savoir, but the main task in this period has been the design and implementation of SOFA in the AI toolkit ART. The first stage was to duplicate Savoir's inference mechanism and to represent two of the six finance options. A graphical interface was added, based on a user-controlled display of the network of dependencies and the use of meters to show desirability of options. The interface is intended to allow immediately understandable and versatile explanations. After refinement of this interface, the remaining finance options were then added.
The system has been successfully demonstrated to the IKBS Director, to the ALFEX club (RAL hosted their final meeting) and many others. A poster was produced for the Alvey conference.
The knowledge engineering documentation from an early phase of the ALFEX SOFA has been examined with a view to an ART reimplementation which will make explicit the metalevel reasoning and possibly represent concepts of financial interest such as risk. Also a study of ART's viewpoint facility has been made, with the aim of determining its applicability to implementing functional changes in SOFA.
A proposal for a 1 year extension to PARALFEX has been submitted to Alvey.
An IFE proposal was accepted at the December round of the Building sub-committee, with a start date of April 87. This is a collaborative project with Strathclyde University, with 1 man for 2 years at Strathclyde and 1 man-year at RAL. The project has been divided into two, a MMI oriented development effort at Strathclyde, and an IKBS oriented research effort at RAL.
The research at RAL is looking at the designers and the packages, (or package developers) conceptual structure of the domain knowledge, with the objective of producing a mechanism to map between them. Project plans have been drawn up both for the research at RAL and the liaison with Strathclyde. A trial run for the acquisition of the domain knowledge was (and is being) conducted, and arrangements are being made for access to the experts. One spinoff was the development of tools to aid this task (see below).
During the last year, this project has progressed from the early exploratory stage to an almost usable system. At the moment, working, and tested, software is available for:
Work on an inference mechanism for conceptual graphs is well under way. Close links have been established with other groups around the world which are working on CGs. There has been some spinoff from this project in the development of diagramming tool (see below).
In the course of the above research, and in response to external contacts, several useful tools have been produced, or are at advanced stages in development.
A small system has been built using the expert system shell SAVOIR to aid in short listing applicants for computing jobs at RAL at SO/HSO level. Huge numbers of such applications are frequently received in response to ' job of the month' advertisements and the aim was to provide a system which a clerk or secretary could use to help decide which candidates should be shortlisted. The completed system was rather limited in scope but undertaking it did provide useful experience both in the use of SAVOIR and in building expert systems.
A PROLOG program was built to configure devices in the OPAL experiment on the LEP ring at CERN at the request of members of High Energy Physics Division. This was reported in IKBS/TN11, and is being prepared as a RAL report by REP division personnel who have further developed the prototype which we prepared for them to show that the problem was comparatively easy to solve using AI techniques.
MBD (together with some help from MDW on knowledge elicitation) has built an expert system to advise inexpert staff in running up (conditioning) a new ion source for ISIS. Ion sources are capricious devices and the expertise of the two experts involved was something of a moving target. Nonetheless a system was created, first of all using the Xi Plus expert system shell and finally using the Crystal shell. The use of Crystal proved an interesting experience because of its very high productivity, and it was this system which was eventually tested by the ISIS staff. It proved valuable except at a particularly difficult stage of the operation when events moved quickly; an on-line system would probably be needed to cope adequately with that stage.
The high productivity of Crystal was used by MBD (with GAR and SCL acting as domain experts) to build the Alfex Club's Source of Funds Advisor (SOFA) in Crystal. The task was undertaken extremely rapidly and successfully demonstrated to the Alfex Club when they visited RAL in May. Since that time MBD has added a fuzzy logic function to Crystal and the system now fully emulates the SAVOIR version.
Throughout the year, several potential areas for future research were investigated. Some of these proved worthless, others were rejected by funding sources or collaborators, while others are still being looked at.
The work reported here is carried out by what is now the Infrastructure Section together with Cyril Balderson working directly for Ken Hartley. The main objectives are:-
This is becoming an increasingly management dominated activity with support for GEC Series 63 being carried out at EUCS (formerly ERCC), the VAXes being stable on BVSD 4.2, UTS not moving to System V and Sun support being sub-contracted to the Common Base. Furthermore the systems expertise which was needed to support GEC 4000 and Prime machines has also ceased to be of importance as machines are phased out and support moved elsewhere.
However the UNIX and Communications expertise which has been built up in the early days of the programme continues to be of vital importance to the Division (through IDUS development work) and the wider community.
The staff currently in post are:
The Section suffered two major reorganisations during the year. In November, the Divisional reshuffle meant that Francis Yeung took over responsibility for both the GEC 4000 and the Prime Systems from Mike Claringbold. By this time, GEC systems support had dwindled to just one person, following Shirley Wood's promotion and move to the Network Executive. However, the decision to cease GEC support and to pass Primos support to UMIST caused another change in April, leaving the team very short of personnel. This is now being rectified by recruitment and internal transfers. Hopefully, we can now look forward to a period of relative stability.

This year marks the end of an era, with support of Primos and OS4000 finally ending at RAL. These systems have served us well and have allowed large numbers of systems staff to cut their teeth over the years.
The activity on Primes was split between Jeremy Isserlis (Primos) and Mark Roberts (Primix), with help firstly from Mike Claringbold and then Francis Yeung. Jeremy finished modifying and testing revision 19.4.10 of the Primos Operating system, which was passed to UMIST for distribution as usual. This work prompted him to produce a paper on the organisation and administration of the Prime computers at RAL, and action is now being taken on his findings. Revision 20.2.la of Primos arrived in December, and the SERC mods inserted. Just as this was done we received revision 20.2.2, which was modified similarly. Testing was longer winded than formerly as new disc partitions etc. were also necessary. Again, this work led to the production of a discussion paper, this time on the need for the modifications. As expected, this proved an emotive issue, and was discussed at length. Some progress was made in classifying the changes, but further work in this area will now be undertaken by UMIST, following the decision to hand over responsibility for Primos in April. Thus ended some 10 years of involvement with Primos, but sorrow was tempered with relief (particularly in respect of the SPARS (Prime error reporting)!)
Once version 19.4.10 had been completed, Jeremy and Mark installed the new system on Technology Division's new P9955II that replaced the two P750s, RLPG and RLPI; this work included merging the systems software of the two old machines and assisting operations and the local manager. Later, they helped install a floppy disc device in place of the old card punch machine used to transfer data to the wire wrap machine. RLPD, the Prime development machine, received a streamer tape drive at last. The library wanted a demonstration of the PRIME INFORMATION database system (a version of PICK) and a library package, BOOKSHELF, on RLPA for a sales demonstration. Jeremy mounted this, with little help from Prime.
As well as helping with Primos, Mark completed the Primix beta test report on Primix 2.0. The effect of this on Prime was considerable, and involved going to Prime US to assist with the solution to some of the problems. This has proved to be very useful for both sides, and hopefully the contacts will be retained. Speed still gives the major cause for concern however. Mark made a number of suggestions which Prime have now included. The released version eventually arrived at the end of April, and was installed on the development Prime running with SERC Primos revision 20.2.2. Benchmarks using the Byte and Aim tests have been carried out, along with measurements intended to estimate the impact that Primix users will have on Primos performance. A number of bug reports and enhancement requests have been submitted to Prime. A trial user service on RLPA began in July. The Beta test version of Primix 3.0 with Primos revision 21 has recently been received. It is hoped that the performance and functionality will be sufficiently improved for a reasonable service to be offered on ECF Primes. It is planned to reconsider the whole issue at the end of September.
Last year, RAL commissioned Salford to provide an implementation of JTMP which would interface to the SERC networking code. This was monitored by Eric Thomas, with UMIST providing the necessary interface routines. After some delays (on both sides) it passed its acceptance tests, and is now available for release to sites. Note that it is a RJE implementation only; you cannot send jobs to a Prime via JTMP.
Following the departure of Neil Davidson, Shirley Woods and Chris Rust continued to provide the general systems support for the GEC 4000 series. This included work on the NRS naming scheme. The move of Shirley brought the team down to a membership of one, and it was decided to plan for the freezing of the System. It had been hoped that the next version would be mounted, and the GEC X25 would be provided, but in the event neither proved possible (in spite of an attempt to use contract help).
It was finally decided to leave the main system alone, but to fix as many mail bugs as possible before April. Chris completed the work, and another era came to an end!
Most of the year has been spent on two activities: trying to get UTS/V into service and mounting TP4/LLC1. Stanley Ooi worked on these for the short time he was with us, along with Neil Calton and David Hicks, who carried on the work when Stanley left and Neil changed job.
A new version of UTS/V (1.1. 2) was mounted, and various packages ported to it. This was not always an easy job, with the 4250 backend proving troublesome. A new accounts program was introduced to correspond with the requirements of CCD. Much effort went into improving the documentation and in creating a proper boot tape. The discs were reorganised so that the minidisks were of a suitable size to be included in CCD's normal dumping schedule. Further changes were brought about by a new version of CMS, which affected the FTP and Mail system.
The two major hindrances to the introduction of UTS/V were the mounting of Franzlisp (only a binary version had been available under the old UTS) and the provision of full-duplex terminal lines. Franz has now been mounted, and Cambridge are being assisted in porting their code (HOL, High Order Language). Amdahl tell us that, at last, there is a version of UTS/F which coexists with the Compro software in the front-end which will allow local terminals to have full-duplex access. As yet we are unable to verify the above. This is at least a year late.
In order to provide better access to UTS, and to test out the ISO LAN protocols, the ERCC TP4 code was mounted over LLC1 via an Auscom box which links to a fibre optic link from the Atlas Centre to R1. The York Coloured Book software was used to provide file transfer and remote login. The work was complicated by the need to share access with both CCD and HEP, and hardware problems with the Auscom. Finally, files have been transferred between UTS, a VAX and a SUN running ISO, but not before differences of interpretation of the standard had been encountered (and solved). Unfortunately, remote PAD login has proved more difficult, and is still not working correctly.
Attempts at getting UTS into a state where it will be more useful have been going on for a long time now. Regularly, the need for UTS is reviewed. There is one external project that has made extensive use of the software, but this is due to end shortly. It has been decided that UTS will be withdrawn by March 1988. The increased power of single user workstations and the availability of the CRAY X-MP makes a UTS service much less attractive than two years ago.
Neil Calton has been working on various text processing projects during the year. When he moved to Communications in April, Chris Rust (late of the GEC) took over. Neil has written shell scripts to enable UTS users to format documents with titroff and its preprocessors, and obtain the output on the IBM4250 erosion printer. A user's guide to the IBM4250 and formatting documents on UTS has been written and distributed. This includes information on fonts and character sets. The facility for accessing the 4250 from rlvc has also been enhanced. He has also adapted the UTS mv macro package to enable viewgraphs for foils and slides to be produced on the IBM4250. A user's guide to this mv macro package, with several examples, has been written.
Neil has installed, adapted and tested the TRANSCRIPT text processing package on UTS/V. As UTS/V is not yet connected to PostScript printers via the Ethernet various changes have had to be made. All Postscript output is redirected to the standard output channel. Facilities have been provided to assist users in transferring PostScript files to other machines for printing. A paper and a User Note have been prepared.
Neil helped connect a pragma QMS PostScript printer to rl.vf and tested it for compatibility with the Apple LaserWriters. He has also been trying to solve some of the flow control problems that have cropped up with the a13 LaserWriter. In addition, he installed and tested titroff and its preprocessors on rl.vm running Ultrix and tested them in conjunction with the Transcript software.
Chris has mounted the DWB 2.0 text processing package on UTS. Following this, he did the same on rl.vm, converting the package from a System V environment to a BSD environment. The most difficult part of this process was the conversion of two indexing programs which were particularly dependent on System V features.
Work on the VAXes has mainly been the fixing of bugs, reported locally and at the remote sites. The loss of both Simon Frost (at the end of last year) and Jim Aitken (November) was keenly felt, since they were the acknowledged experts. The team managed as best they could, and continued to improve their knowledge. Francis Yeung, Ian Harding and Neil Calton had the most involvement, with Ian and David Hicks specialising in Ultrix. Since April, Mark Roberts has begun to look at BSD Unix, mounting the latest version of C++.
Various versions of Ultrix have been mounted, and Ultrix 2.0 is awaited. Benchmarks have been run. Ultrix was successfully mounted on a Systime VAX, and might be considered a candidate for other VAXes if DEC can agree to quote us a price. Although DEC took over maintenance of the hardware, they are very reluctant to agree to running DEC software on a 'modified' machine. However, since we seem unable to obtain BSD 4.3 (because of the US export clause problem), Ultrix may be the only way of getting the VAXes to run faster. The longer we leave it, the less likely it will be, since the VAXes are becoming less important.
The VAX team also provide support for the Pyramid, including the addition of various SERC mods to the standard OSx (we must take care not to get into the Prime position here!) and updating the operating system twice in the period. An accounts presentation program has been written by Mark to assist in the introduction of accounting to what is part of the Gold service.
The 3B2 has proved very useful as a System V reference machine. Francis has installed Sys V Release 3 on 3B2 with a borrowed 5620 terminal (the original one has to be sent back to Olivetti for repair!). There are a number of new features in the new release including remote file sharing, streams, AT&T Transport Interface, shared libraries, AT&T windowing utilities etc. It has so far proved impossible to allocate any time to SVR3, but there is still a hope that we will be able to evaluate the new facilities. Access will be considerably improved when the machine is connected to the ethernet.
The Division has obtained an IBM 6150 Unix PC. Francis has been involved in the evaluation. The work was concentrated on three main areas user/administrator commands, system calls and library routines. A paper which compared the system calls between the 6150 and AT&T 3B2 (a reference machine for System V implementation) was produced. A plan to produce a similar paper on library routines was withdrawn because there are not enough discrepancies between the two systems to warrant it. The differences in the administrator commands are to a certain extent the results of the trend that everyone is trying something different nowadays to make the interface more user friendly. The absence of the shl (shell layer) facility is more fundamental as the 6150 chooses to have its own 'virtual terminal' facility instead. The printer spooling system on the 6150 is also different from that on the 3B2 and that appears to be a deliberate decision too. One interesting command that is not available on other systems is confer which provides the users with an on-line conferencing facility.
The main problem with the 6150 at the moment is communication as it is not connected to other machines by any means. However. with the cartridge tapes, there have been some successes in transferring files from the Sun3 workstations to the 6150. The problem should be resolved when the 6150 is connected to the Ethernet.
A quick comparison of the Byte Benchmark results between the Sun3 and 6150 shows that the Sun3 is faster executing function and system calls but the 6150 is faster running shell scripts. It would be interesting to compare the performance of the two systems with some genuine application programs.
Recently, IBM have expressed an interest in a joint project with the Division. Francis will lead the team which will look at connecting a Transputer, and using the resulting system to run some of the standard packages used by the Magnet Design team.
As part of the RAL A.S.O training scheme, Duncan Green has been given the task of providing an Online System Activity Logging facility. Before departing Stanley Ooi had proposed and devised a scheme where all changes to development systems would be logged in separate binders on a standard form. Envisaging a large growth of paper and the benefits of holding all the information in online relational format, it was decided that a better system should be provided. Duncan is using the Ingres Relational database, which is not the easiest database to get to use. He has successfully managed to develop a skeletal system via a C program interface which performs the basic operations such as retrievals, additions, perusal etc.
For much of the year, the Communications team has been seriously understaffed, reaching its low point when Jim Aitken left in November. The November reorganisation added Tony Lowe to the team, and now all the communications services, including basic wiring, are organised from within Infrastructure section. The April restructure changed things considerably by moving Jeremy Isserlis and Neil Calton into the team. In addition, efforts have been made to arrange a sabbatical year for Danny Smith from the University of Queensland to work within the section on X.400 mail protocols. This has proved successful, and he will start at the end of August.
Mike Woods, having left the team in November, rejoined in April.
Ian Johnson carried out extensive testing of the York X.25 code which he had ported to run with the Morning Star board on the Pyramid. This testing showed that the Morning Star board could provide a reliable X.25 connection, and a user service was introduced on pyr-a in early November. Shortly after this, he visited Brunel University and mounted the York X.25 code on their Pyramid. At both sites, the service provided is two-way FTP, and incoming terminal calls.
In December, Pyramid mounted a new revision of the X.25 Front End code, which runs on the Morning Star board. This revision totally destroyed the X.25 service to users, and prevented any further development or refinement of the York code, such as porting the York PAD program for outgoing terminal calls. Ian made extensive efforts, in conjunction with Pyramid technical staff, to pinpoint the OSx kernel problems which were preventing X.25 working. These problems turned out be due to a faulty upgrade procedure carried out by Pyramid. The Pyramid now runs a reliable X.25 service, including outgoing X.29 using the York PAD program. Pyramid UK have taken over support and development of the changes Ian made to the York netio routines.
Ian commissioned X.25 software on the Pyramid WorkCenter Central Server, nfs4.
In April, Jeremy Isserlis moved into the Comms team, working with Ian. Jeremy evaluated SUN's Coloured Books product for their X25 offering. Although a complete test cannot be made until version 4.0 of Sunlink X25 arrives (currently on order), it was possible to test enough aspects to confirm that the product would be a suitable recommendation for ECF and Alvey SUNs requiring stand-alone X25 access.
Jeremy is now installing software on one of the Division's fileservers, in preparation for moving the mail service onto this machine.
The section has participated in a long-running project to provide ISO Transport Class 4 (TP4) protocols on to the Alvey Infrastructure VAXes. This was undertaken in conjunction with ERCC. Before leaving the section, Jim Aitken finally managed to remove some low-level bugs that were holding up progress, and produced a working system. He also ported the code to the Pyramid and demonstrated VAX-Pyramid interworking. Unfortunately, performance of the VAX system was much less than hoped for, typically achieving only 10-20% of the throughput of the equivalent application based on TCP/IP. This was found partly to be due to an unoptimised kernel implementation of the protocols, and partly due to the use of applications software tuned for WAN, rather than LAN, use.
The original reason for providing TP4 on the VAXes was to allow interworking with the Infrastructure GEC Series 63s. However, the recent appearance of TCP/IP on these machines fulfils this aim. Further development of TP4 on the VAXes has therefore been frozen.
Ian Johnson took part in a beta-test evaluation of SUN's Sunlink TP4 product. As with the VAX and Pyramid work, the York netio interface was put on top of the Sunlink code, allowing Coloured Book protocols to run over TP4. This proved successful, and Blue Book FTP gave throughput levels of 30-50% of those obtained using the TCP/IP equivalent. Ian also managed to interwork Blue Book FTP to the Pyramid, and to UTS (working in conjunction with David Hicks, reported earlier).
Ian Johnson assisted in the initial evaluation of Pyramid's Pink Book product. This attempt was ill-fated, due to problems with the Pink Book implementation on the VMS VAX in CCD. Another attempt has been arranged and hopefully a better result will be obtained.
Bob Day organised the introduction into service of NFS on the Pyramid, and the adoption of a "global user filestore" between Suns and Pyramid. This involved bringing the systems administrators up to speed on what NFS is about, and then getting them to do all the hard work in sorting out common Unix UIDs over the network. Once the licensing had been sorted out, rl.vd was added, and this meant a lot of work for Mike Woods in tidying up his implementation (despite fairly horrendous hardware problems). Neil Calton (having joined the team in April) looked after this work.
Ian Gunn attempted to implement the Yellow Pages distributed look-up system on pyr-a. This proved impossible to do with the current Pyramid implementation of NFS. Another attempt is planned when Pyramid deliver a more up-to-date version in August.
Bob gave two talks on NFS: one to the Alvey site managers' meeting and one to the computing Science Dept. at the University of Exeter.
Mike Woods' last work before his temporary stay in Software Engineering Group was to port SUN's generic NFS code to the Infrastructure VAXes. To prepare for this, Bob Day organised a one-off course from Instruction Set for Mike, Simon Frost and two people from ERCC, where a similar port to the GEC Series 63 machines was beginning. This took place at RAL, and resulted in an initial version being available very quickly. Mike spent some time in adapting existing utilities on the VAX to work under NFS, and in curing some low-level unreliability problems. The port is now in service on rl.vd, with Mike having provided 'consultancy' in getting this going whilst starting his RA work. The port is now being shipped to sites, with Oxford as the field test. Neil Calton has organised the logistics of the distribution. Ian Gunn and he will be doing the necessary site visits.
Neil has also written an introductory guide to NFS with particular reference to the steps that need to be taken prior to its installation at a site. This document was intended initially for Alvey site managers but its scope is being extended to make it of more general interest . Plans are also prepared for the introduction of NFS on rl.vc.
The main problem with the VAX NFS project turned out not to be technical but one of licensing. Negotiations between AERE Contracts and Instruction Set (distributors of the code) proved to be extremely protracted, and involved many people's time.
Ian has spent much of his time converting the news system to run over NFS rather than via daemons as was previously done. He has made available a version of rn which runs over NFS on Vax, Sun and Pyramid computers. He has also fixed many of the problems with news which have appeared over recent months. Ian has installed the Newcastle Connection on the Informatics Division Sun file-servers and has ported the Newcastle Connection to the Pyramid. There were several bugs, most of which have now been fixed. He has also put the Newcastle Connection on the Pyramid Central Server running a beta-test release of OSx4.0, the new release of Pyramid's operating system.
Bob Day visited Pyramid Technology in Mountain View during May to discuss various communications issues. Major topics discussed were NFS (as it relates to the contract with Pyramid to supply Central Servers for the ECF) , X.25 (Pyramid are doing a new one to replace the "Morning Star"), Pyramid/CRAY communications, and Pyramid's ISO OSI planning. This was a very useful trip, allowing Bob to give Informatics' view of communications requirements to the team responsible for all Pyramid's communications products.
Tony Lowe joined the team in November, and has been kept very busy with the many and various communications requirements, caused by office moves, new equipment, additions to the Division (such as half of Technology!) etc. He has also been involved in installing etherPADs and thin wire ethernet. A Spiderport has been ordered so that it can be compared with the Bridge equipment used so far. In addition, Tony has visited a number of the Infrastructure sites to discuss their Communications problems.
Bob and Tony undertook a series of measurements of traffic levels on the ID LAN and its servers. A number of interesting phenomena were discovered. This led to the purchase of a Hewlett Packard Ethernet monitor, which will be used to study what actually happens on the Informatics LAN. A joint study has been set up with Heriot-Watt University to attempt to construct a mathematical model of the LAN and servers, and to test it with data from our LAN. This should give a tool with which to predict what enhancements will be needed to the LAN as more clients are added, thus making long-term planning possible. Hopefully the model will be applicable to all LANs of this form.
Bob Day and Tony Lowe have participated in discussions aimed at setting up a Rutherford site Ethernet. This would allow high-speed access to other LANs on site, and in particular to the central facilities in the Atlas Centre. This work led to Bob and Tony Lowe undertaking the evaluation of LAN bridges devices for LAN interconnection - an interesting task which looks set to continue for some time. So far two bridges have been evaluated. One, Bridge's 1B/2, seems to be a well-designed piece of kit; the other, LRT's Intracomm 6, unfortunately seems to be lacking in performance in its present form. It is possible that Tony and Bob will co-operate in a larger evaluation of bridges being conducted by Daresbury Laboratory on behalf of the JNT.
In November, Ken Hartley was appointed Head of Alvey Infrastructure, on a half-time basis. Cyril Balderson assists him in these duties. The main function is to serve as a channel of communication between Millbank and RAL, and to try to bring together all Alvey Infrastructure activities. As they have been entrenched as separate activities for three years, little progress has been made. Ken and Cyril also serve the Alvey Infrastructure Steering Committee - Cyril is secretary - chaired by Laurence Clarke.
The most constructive effort during the year has been feeding back Informatics Division's experience of Alvey to those planning IT92 and to draft proposals for a new, broader based infrastructure.
At the November reorganisation, Eric reassumed the role of RAL Infrastructure Project Manager, assisted by Peter Hemmings. The main work has involved the running of Site Managers Meetings and the reconciliation of the spending at sites. This last has proved as difficult this time round as it was in the first year, and suggests that one should aim to avoid having site contracts which coincide with the SERC financial year. Peter has also taken over the liaison role with GEC, and as the chaser of other contracts (notably the one for NFS). At April, he was joined by Paul Jeffery, who has been learning fast. Paul has already produced time series graphs and histograms of the statistics from the sites, and has witnessed an Alvey first statistics from everywhere!
With the implementation of the Forty Report recommendations going ahead (eventually, after a lot of hassle with the US), a Cray XMP 48 was installed in the Atlas Centre. Eric and Bob Day visited Cray UK and, following discussions with CCD, Technology Division and others, put together a couple of papers proposing ways in which Workstations running UNIX might be able to interface to the Cray without having to run JTMP and gaining batch access only. CCD plan to run UNICOS (UNIX on Cray) eventually, and there will be a Hyperchannel connection as well. After a slow start, work on providing a Unix interface to COS has just begun.
Bob Day has participated in the ECF Central Server project. From an earlier Operational Requirement a shortlist of machines was drawn up. Bob evaluated the communications abilities of these, including NFS performance tests on the Sun, Gould and Pyramid offerings. (He was ably assisted in this by Mike Woods and Lynton Jones-Ng.) From these, he and Julian Gallop drew up the final Tender Requirements, the responses to which led to the decision to opt for a mixture of Sun and Pyramid machines.
Bob is now involved, with Neil Calton, in a more extended evaluation of a Pyramid Central Server, purchased in March. To date this has involved progressing provision of Pink Book and TP4, as well as chasing Pyramid for performance enhancements for NFS.
Tony Lowe visited Warwick, the first external site due to receive a Central Server, to advise on LAN provision.
Following various disagreements between Management and workers on what facilities could and should be provided in-house, it was decided to identify a Divisional Service. Bob Day played a major part in this, and will be the Technical Development Manager: this seems to mean being responsible for introducing new facilities; tentative plans are for a 'real' mail service, properly integrated text processing, and 3270 emulation from Suns. Bob has also advised on the provision of server and LAN capacity needed for the purchase of an extra 24 SUN workstations for Divisional use.
Ecstasy is the name of a project set up by the Control Engineers to provide a common interface to a number of separate programs. Those with long memories will recall a package called DELIGHT-MIMO which tried to do the same thing. This was rejected by the community for a variety of reasons. RAL has been asked to help in two ways: to provide some advice and programming help on the Window Manager side of things and also to advise on Software Engineering aspects. Tony Williams supplies the former, and Eric Thomas provides the latter service. This has involved the provision of a definitive, quantifiable project specification. None of the other participants appear to have had any experience of writing such a document, and the stated objectives were originally very vague. The current document at least makes it clear what is being done (but there is a possibility that the community may not agree). The first version of the software should go to academic sites in January, with a final version (for handover to RAL) by June. It is still not clear how active a role RAL will play beyond this date. It could involve a large programme of work.
CCD again asked that the Division take the latest batch of ASO Trainees to introduce them to Unix. Eric Thomas and Neil Calton handled this. Eric acted as Customer, and provided the acceptance tests. As usual, this quickly demonstrated the need to plan tests so that errors are found (rather than merely throw one set of figures at the program). Neil also provided a set of twenty questions on UNIX for them to answer.
Mike Woods officially left the Group to join Software Engineering on his promotion. While there, he has begun to look at the possibility of working on a compute server which would locate the best place on the network to run a particular job. So far he has concentrated on the problems of setting up the administrative network needed to provide compute power at arbitrary places in the network. The work has been done using SUN workstations and SUN's RPC (Remote Procedure Call) mechanism as the underlying carrier. Lessons learnt from this include an appreciation of the limitations of SUN's RPC for this type of applications, and the need for a reliable underlying transport service to convey state information between servers. It is clear that a compute server is much more complex than a file server (such as for NFS) in these respects. The next stage of the work is to construct a proper 'worm' server using the facilities provided so far. Mike has decided to recode his software in C++: this is to take advantage of the language's enhanced facilities for manipulating the complex data structures which seem to be a feature of this work. Mike returned to the Infrastructure Group in April.
Mike Woods has been supervising one of the ASO Trainees (Arif Hussain), who has been developing a 3270 emulator for the SUN. After the successful completion on the project, Mike did a small amount of work to bring the emulator to a state ready for distribution. This included tidying some of the code, altering the makefile to aid installation, and ensuring the documentation was complete. All work is done and the new release of the emulator is now available on the Suns.
Keith Bartlett, Alvey Infrastructure and Coordination Director, has set up a small team of industrial secondees to advise on the use of Open Systems for national R & D Programmes. OSST - Open Systems Support Team are mainly concerned with communications between industrial sites and interworking with JANET and other European networks. Ken Hartley, Bob Day and Eric Thomas had a fruitful discussion with them and have provided input to them on various strategy papers. Eric gave a paper, alongside OSST and the Network Executive at the UMIST meeting of the Alvey Networks and Communications Club, which discussed communications infrastructure for Alvey and similar programmes. It is hoped to continue this close collaboration in future. Cyril Balderson is preparing a paper on communications links between RAL and the outside world, as an example of the kind of problems they face.
During February, Cyril Balderson undertook the Project Managership of the Alvey Mail Service. Unfortunately, this has not always been held in the highest regard by its users, for various reasons. Although the service may have a limited period remaining with closure at present assumed for late 1988, it was felt worthwhile to specify a number of changes to the user interface to the service. The paucity of person-power however (10% of Shirley Wood!) has meant that these changes are still to be completed. A major activity was to reduce the user-base to those who had actually used the service within the last 6 months which caused a reduction of about 50% from those originally registered. There are now about 350 users registered, and among these there is a steady level of use.
A publicity piece for the Alvey Mail Service has been written for publication in Alvey News (probably October).
The Division has requested that an automated means be found to generate the financial reports received by Project Managers from the official RAL data. Peter Hemmings is undertaking this work, and has produced a user requirements specification. A functional spec will be produced shortly, and it is hoped to finish the system in time for the next end-of-year panic.
C Balderson The Alvey Computing Infrastructure Project, Alvey News.
MIW continues to attend a MSc Course at Brunel University one day a week.
Next year is bound to be a year of transition. There will certainly be a substantial run-down of Alvey activity; what remains unclear is whether there will be a follow-on programme of the kind envisaged in the IT86 report and, if so, what role RAL will be asked to play in it. KFH has been responsible for several drafts of an Infrastructure Strategy paper, each one modified by the Steering Committee. The end result is a rather different infrastructure from the Alvey one. One of the proposals is the setting up of a common base of software for the IT community, which would include everything from systems and communications up to environments and IPSEs. Creating and supporting it would bring together the contractual, managerial and technical skills of the Division. this should also fit in very well with work to establish EASE in the Engineering Board area.
Considerable effort has been expended in trying to ensure that Informatics does have a part to play in IT92. However, other avenues are also being explored to find work which is challenging, appropriate and above all, funded!
The section's interests lie in the general area of user interface design on advanced workstations, undertaken both by doing R & D work in the area and by supporting relevant research work elsewhere. The major funding areas are:
Apart from Arthur Seaton, who has returned to Edinburgh for love and golf, section membership has been stable. Keith Appleby has recently joined us as a student working for Mark Martin. Staff currently in post are:
Both Helen Jenkins (HVJ) and Rita Hollington (RAH) have provided effective secretarial support during the year.
Following the recommendations of the Workshop on Window Management that the section organised which was held in April/May 1986, approval was finally obtained from the ci-devant Alvey HMI Directorate for work to proceed at RAL. The project's objectives are two-fold: (a) define a low-level software interface (known as the Client-Server Interface or CSI) to window management functions imp1ementab1e on a range of workstations, and (b) implement the CSI on selected workstations as an existence proof. With vendor support for the CSI, application toolkits such as WW, which at present require extensive work to port to new environments would become much more widely available, easing greatly the work of applications programmers. Phase (a) is now complete with the publication of RAL Report 87-017 which has been widely distributed (CKC, CAAG, ASW). The implementation on the PERQ (with limited functionality) is complete. The SUN implementation awaits the arrival of X version 11, but some design work has been undertaken. A paper has been prepared comparing X and the CSI. Work on the design of a layout manager which runs on the CSI has also begun, with some prototyping of user interface ideas on X being undertaken.
Robin Milner's group at Edinburgh have a reputation for good formal methods work. Lately they have rea1ised that a good user interface is necessary for effective take-up of their work by ordinary software engineers. Following some discussions and presentations by RAL staff (ASW, KR, DAD) at Edinburgh, the Alvey Software Engineering Directorate agreed to fund work at RAL to provide a user interface for the CCS concurrent programming workbench. A limited amount of work has been done on this, mainly by ASW, HMM and CMC.
MMM has continued to work on this graphical toolkit, aimed at applications programmers needing tools to write highly interactive applications. WW now supports colour, full screen access for reading and writing, and large cursors. Some of the work has been done in support of the porting of RAL GKS to SUNs. It has also been ported onto the CSI. Spin-offs from the Alvey Demonstration work (qv) into W include optimising window updating and bitmap access.

Experience with the SPY screen editor has led to MMM writing TEN, which gives more screen real-estate back to the user, as well as better functionality based on WW improvements such as files tore browsing, menus, cursors, small text areas and cut and paste with the window manager. Some optimisation has been possible to give dynamic feedback when sliding windows, and a simple experiment with gesture recognition was undertaken.
CMC has tweaked MON to fix a few bugs and add some facilities.
CAAG issued the first release of the PostScript interpreter near the beginning of this reporting year. Since then a number of improvements have been made, including non-integer scaling, arbitrary rotation of bitmaps, the setscreen function, fast area fill and complex clipping. Optimised text printing has also been provided - this gives a speed up of about four times. Ports have been done to Whitechapel, Orion, Vax and Pyramid (these last two permit remote viewing). The system has now been released publicly.
The whole section contributed to this activity a demonstration suitable for the Alvey Conference to show off our work. The demonstration consists of a small play, showing how a remote researcher can co-operate with a local technician on the design of a fairly complex laser facility (thanks to Denis Nicholas in Laser Division for providing the technical 'props'). The play requires two high bandwidth networked workstations, and assumes a voice channel is available. The major elements of the demonstration include MUSK, a multi-user sketch pad which allows a number of users to construct diagrams, free sketch, and even input text, while sharing a common working area; DESED, a highly interactive laser design program; and PIXVIEW, which acts as a software video camera, enabling one user to see part or all of the screen of another (by consent, of course). ASW, MMM, CMC and CAAG did most of the software. The demo 'script' was handled by KGD and TC. The necessary PR material - display boards and handouts - were generated by ASW, TC and KR. Overall, everybody commented on almost everything. KR did a sterling job of worrying about the deadlines.

Although this was a fair amount of work, the end-result, which is acceptably smooth, on its own justifies the investment. In addition, the opportunity was taken to explore in a small way problems associated with group working and communication; this has already resulted in work to be presented at a forthcoming conference, and bids to be a good research topic for the section in the future. As a final note, if WW had not been available then the project would not have been feasible.
CAAG continues to act as Mailshot Coordinator, with KR trying to sort out major problems as necessary and RAH providing the organisational back-up (arguing with Photo/Repro etc). Towards the end of the year an editor for the HI proportion of the mailshot was finally organised as part of the Loughborough LAMMIC contract. This has inevitably generated some discussion, particularly as LAMMIC would like to provide a monthly newsletter rather than part of a quarterly mailshot.
CMC looks after this; contributions and usage are currently at fairly low levels. Some 40 tapes are in the library.
This project aims to provide access to information on MMI research interests and services in the UK. KGD took over the project from Arthur Seaton and has done most of the direct database and form design work. 'Te has also spent time using awk and refer to ease the task of getting data into the system. Following comments from a number of experts, the original form was extensively redesigned and distributed to about 700 addresses. In parallel the database, using the INGRES DBMS, was designed and a set of image processing researchers' data input, partly as an exerciser and partly to satisfy a requirement for a paper copy by the Image Processing co-ordinator. This required writing a set of awk programs. Considerable difficulties were experienced both with the public-domain INGRES itself and the various implementations on the Vax and Pyramid. Occasionally the Pyramid version would disappear due to system vagaries, sometimes known as upgrades. The decision has just about been taken to purchase the (affordable) SUN version of INGRES; this would provide not only a more robust environment but also vastly improved front-end facilities.
TC now looks after the Alvey Human Interface Club Steering Committee, now revitalised under Vic Maller's chairmanship. As well as the usual secretarial duties, this has also required organising an HI Club meeting in London in March, and some support work for the nascent HI Special Interest Groups. The HI Professional Bodies Liaison Group is also supported.
Bide, IT86, IT92, Alvey 2 are all aliases for the same thing - the follow-on programme to Alvey for UK IT support. Following publication of the report, the Alvey Human Interface Committee set up two working parties to look at research requirements and organisational exploitation issues respectively. KR (as secretary) and FRAH attended the first-named working party, which met fairly frequently over a period of some few months at the beginning of 1987. The reports from the two working parties were merged and KR has a few copies if anyone is interested. As a document specifying research to be undertaken, it probably lacks a clear focus.
PUMs are Programmable User Models these are things that the interface designer might have to program in future to see how good or bad his interface design is. (Think about an architecture which has memory which 'forgets' if you give it too much to remember). Richard Young at the MRC Applied Psychology Unit at Cambridge is undertaking this work with Alvey HI funding. KR is the Monitoring Officer for the project.
Two proposals have been submitted by the section to SERC - one to the Computing Science Sub Committee on Extensible Graphical Programming, and the other, collaborative with Leeds University Chemical Engineering Department, to Process Engineering Sub Committee B on the use of advanced user interface techniques for a complex plant design problem. Despite severe pressure on CSSC finances, the first proposal was mostly funded - a tribute to the skills of its writers (ASW, 'TC). The second was not fully understood by the Sub Committee, who to their credit did not reject it outright but appointed a panel to visit RAL. For various reasons outside the section's control and understanding, the visit planned for May/June never quite happened and is now scheduled for 25 September. This year, that is.
A meeting with staff at the Technische Hochschule, Darmstadt was held to consider possible topics for a European Twinning proposal. KR, DAD, JRG and CJP all attended, and a proposal on the general topics of Theory and Practice of User Interface Design is being prepared, mainly by KR.
Some longer-term thinking has also been taking place on the future research directions for the section. These involve high-power workstations, multi-media input and output, and high bandwidth communications to remote multi-media resources. Various funding sources are being considered, including IT86, ESPRIT II, and so on.
There have been a number of delays in this area, some due to availability of suitable equipment, and some due to lack of space for a proper HF Laboratory (IGLM please note). MJP and 'TC have been working on some aspects of visual illusions, which are intended to lead on to investigations of different on-screen manipulation styles and 3D effects, related to exploration of complex spaces.
At the time of writing, four-sevenths of the section is in Amsterdam at this conference. There is an associated Workshop on Higher Level Tools for Window Management, of which ASW is programme chairman. MMM, CMC, and CAAG are all giving papers. ASW will also be acting as a panel chairman at the Conference to report on the Workshop.
The usual collection of things that do not fit neatly above are reported on here.
Exploitation of RAL Software. There has been much discussion but little actual progress with BTG on the exploitation of WW and associated software. KR has probably suffered the most. ASW did manage to persuade ICL to allow spy to be distributed to commercial companies (for internal use only), however.
Typesetter Service. KR and ASW were involved in discussions with Admin Division and CCD on the needs of the Laboratory for a high-quality typesetting service, and the subsequent purchase and installation issues. A Linotype Model 100 is being bought, which is a PostScript-driven device. The minor details of actually providing a service are now with RET and his section.
C++. Release 1.1 was ported by CMC to the PERQ and Pyramid, and some discussions with NBC have taken place so that Systems can do subsequent ports. CMC has ported release 1.2 to the SUNs and the Pyramid for HCI use.
PERQs and Communications. CMC has worked, with Robert Stroud's help and advice, on adding a UDP/IP driver to PERQ PNX5. This allows Ethernet links to the Divisional BSD machines using the Newcastle Connection. This has now been packaged and documented for use outside RAL.
Divisional Distributed UNIX Service. Both ASW and KR contributed to the policy document for what became IDUS. KR also attends ULM.
Know1edge Representation Book. ASW contributed two chapters to this, and TC one in collaboration with MDW.
UIMS Survey. ASW, TC and KR cooperated on the gathering of information for the ECF Programme. ASW is now working with M.1P in generating assessment criteria and a detailed assessment of the products.
ECSTASY. This is a project at UMIST on which ASW provides consultancy on user interface issues.
The following projects are envisaged for the coming year, given funding:
The policy and budget for much of the work of the EC Group is determined by the Engineering Board's Computing Facilities Committee (CFC) . The latter is advised on technical matters by the Computing Facilities Technical Advisory Group (CFTAG), which was established in December 1986 and also met in February and May 1987. The ECFE is responsible for providing input to these groups and for executing their decisions.
The ECFE does not correspond to a particular branch of the group and the following staff participate:
From the ECFE, MRJ and ADB attend CFC and MRJ, ADB, JRG, GAL (secretary) attend CFTAG.
The major concerns of CFTAG have been:
CFC Meetings:- 10 October 1986, 11 March 1987, 3 June 1987 (MRJ, ADB)
CFTAG Meetings:- 11 December 1986, 18 February 1987, 7 May 1987 (MRJ, ADB, JRG, GAL)
Staff as at the end of August 1987:
What the section lacks in numerical strength it makes up in quality! Linda Reed joined the section in April as a half-time mature trainee and has spent all her time in a training mode.
GAL acts as secretary to the advisory group and in addition to the routine paper writing tasks associated with the role, has analysed the data and produced a report on the Applications Software Questionnaire which will be published as a RAL Report in the Autumn. Data on the use of International Networks by the research community is also being collected and a further report on the subject will also be produced.
As part of the Applications Software Review, a series of four Workshops are being arranged by GAL. The first, on User Interface Management Systems (UIMS), takes place in Glasgow in September, with a further one, on Database Systems, planned for November/December. Two further workshops are planned for early 1988.
GAL has now become involved in the management of the project and this is expected to take up to 50% of his available time.
GAL remains responsible for the initial scan of all computer related grant applications referred to RAL for comment. After a successful visit to Central Office, Swindon by Chris Wadsworth, Peter Kent and GAL to comment on all grant applications from the Computer Science Sub-Committee, it is hoped to extend this practice to all committees as this achieves a significant time-saving for everyone involved compared with the current practice of grant applications being sent to RAL in a number of batches.
Fran Childs (FMC) acts as editor of the Newsletter - with 4 editions produced so far this year. Contributions to the newsletter have been produced by members of the ECFE and from external members of the Engineering Board supported community. Production and distribution, against an exacting timetable, is a major task, as approximately 2,500 copies of each issue are distributed.
Fran Childs (FMC) is responsible for the loan pool of the Initiative, which has seen a period of "frantic" activity during the past few months.
One meeting of the newly formed Engineering Computer User Group (ECUG), created from the ashes of the original hardware base committees, has been held (organised by FMC and GAL) with a further meeting planned for September. Attendance at the initial meeting was in excess of 100 which has been very satisfying as involvement with the original committees was declining rapidly. It is anticipated that the format of the ECUG will evolve to meet the changing needs of the user community.
GAL still has some residual involvement with the management of the old ICF/UMIST site management committees and subsequent contractual work. Plans are now being made for the gradual reduction of the level of support obtained via the Support Contract at UMIST. All three contracts let to provide various software items for the GEC series 4000 systems have been completed.
Semiconductor Materials and Devices, Davos, Switzerland. 31/8 - 4/9/87. (GAL)
The Computing Applications Group (CAG) transferred from Technology Division to Informatics Division on 1 July to become part of the Engineering Computing Group under Mike Jane. Bill Trowbridge (CWT) , the previous leader of CAG, left RAL on 30 June to devote his efforts to Vector Fields Ltd, a company which he set up in 1984, and which has recently moved to new enlarged premises in Kidlington. Prior to his departure CWT, who held an individual merit appointment, had been employed half- time by RAL since June 1986. Most of the day-to-day running of the group was in the hands of Alan Bryden (ADB) as Deputy Group Leader as well as representing the Applications Software Programme at CFC and CFTAG. ADB also represents RAL on the Computational Fluid Dynamics Advisory Group (CFDAG), and is closely involved in the discussions about an IDF or Research Programme centred at Birmingham.

The work of the section combines first-line support of a number of commercially provided packages, in-depth support of RAL written software and further developments to cover future requirements.
Staff list:
The PE2D package has been further developed by Vector Fields Ltd since John Simkin and Chris Biddlecombe left the group for this new company, and it is their version of the software which is now supported. The new versions of the analysis modules have been mounted on the IBM mainframe by the section.
This package has now been mounted on the CRAY XMP by CJC with assistance from Alan Mayhook of CCD. Some of the improvements in coding have also been used to speed up the IBM version by about 30%.

Members of the section have taken part in the work to develop and test a suite of software for eddy current analysis in 3D. This is the subject of 3 different collaborations:
A neutral file specification has been agreed between the various collaborators as a means of interfacing the packages with the pre and post processors. This means that benchmarks containing the same input data may be run on more than one package. The Alvey projects for process and device modelling of silicon chips are adopting the same neutral file format. KPD has written a set of Fortran subroutines which read the neutral files and can be called by an interface program.
A post viewer program called HEXTET was written at Imperial College. This takes the output from a 3D finite element program and subdivides the mesh into tetrahedra and then allows the user to display results on any desired plane. CSH has tested this program and made a number of improvements to assure the reliability of the mesh subdivision process. For the international eddy current workshops a number of benchmark tests have been agreed. CJC has been solving some of these problems analytically. CSH has been running CARMEN and NJD has used PE2D for tests where appropriate.
Two courses for users of the RAL electromagnetics software have been held at the Laboratory. The first of these was in November and the second took place in July. Staff from Vector Fields Ltd and members of the Section, augmented by Chris Emson, provided the tuition. The November course was attended by about 17, comprising 8 from UK universities, 5 from commercial firms, 2 from CERN and 1 each from RAL and Milan University. For the July course there was an attendance of seven. Of these 6 were from UK universities and one from RAL. The reason for the drop in numbers is that VF now run their own courses at Kidlington.
First Line Support is provided by members of the section.
This package continues, on the IBM system, to be the main tool for structural analysis. Version 65 was delivered in August and includes a more efficient eigenvalue solver using the Lanczos method. We have considered the possibility of putting NASTRAN on the CRAY but the price quoted by McNeal Schwendler is unacceptably high.
This package is provided free by CEGB and is particularly recommended for thick shell problems. It is installed on the IBM and interfaced to FEGS software.
This package is being mounted on the PYRAMID computer both as an assessment of its capabilities as a structural analysis package and also to gain some experience with implementation on a UNIX system.
These pre and post processors are now renamed FAMBUILD and FAMRESULT and are sold as part of the integrated FAM system. This has been mounted on the PRIMEs, although a version for the SUN may be purchased soon. They are also being used for a number of applications in electromagnetics and device and process modelling. A demonstration of the new FAM system was given in the Atlas Colloquium in July.
This is a module for error analysis which is being written by NJD. It will read a FEMVIEW input file and create an additional file for display of error estimates by FEMVIEW itself.
CSH has carried out tests on the BEASY boundary element package to assess its suitability for inclusion in the structural software to be made available to users. It has been decided that it should not at present be supported.
NJD and KPD assisted in the evaluation of SDRC software for laboratory projects, particularly as a CAD system for the space programme. They provided benchmark problems and advice for laboratory engineers.
S K Chanda, N J Diserens. A Post Processor for Error Estimation in Static Analysis. RAL-87-?, September 1987.
C R I Emson, K P Duffey, J L Marsh. RALBIC Neutral File Read and Write Routines. RAL-87-?
C S Harrold. Using the Concept of Linkage of Closed Loops to Determine the Topological Invariants of a Cutting Graph. Paper to Compumag, Graz, Austria, August, 1987.
Subodh Chanda (SKC) is completing a PhD at the Mechanical Engineering Department, Birmingham University. The subject is Finite Element Analysis of Orthogonal Metal Cutting, and he hopes to finish this in May 1988.
Kevin Duffey (KPD) was promoted to HSO in December 1986.
At present, the Section has 5 permanent staff:

In addition, for the whole period, we have had the assistance of a student from Sunderland Polytechnic, John Mountain (JBM).
This project occupies MM, DT and JVM for most of their time, and BC for 25% of his time. The Project, which started in November 1984, has as its main goal the specification and development of software interfaces between various CAD systems, and between CAD and Finite Element (FE) analysis systems. The present contract ends in October 1987; arrangements are under way for a two year extension. Twelve industrial and academic organisations from six member states of the European Community are involved. Much of the specification work has been completed, and interfacing software is now being developed. The Project has a high standards content, hence DT and JVM participate in International Standards Organisation committee meetings, and BC represents the Project at British Standards Organisation meetings on product data exchange.
The second line of work, pursued by ADI in support of the thermal modelling community of the SERC Building Committee, is the analysis of multivariate time series systems and the development of an Energy Kernel System (EKS). The EKS is an example of what may be called generically "Design Environments" and is intended to test the hypotheses underlying such environments in one particular applications field; namely energy in buildings. Development of the EKS has been approved in principle and funding is being sought in the current grant application round to enable some six institutions to embark on this collaborative project. It is intended that the EKS development will have two phases. During the first phase different strategies will be explored using principles of rapid prototype development. This first phase should establish some best candidates for a working EKS. In the second phase a validated EKS will be produced. In both phases the EKS will be available to academia, the fuel supply industries, other government departments and industries for comment, appraisal and feedback; this should enable the information barrier between academic research and industrial use to be overcome.
It is anticipated that work on environments will expand into other disciplines, such as finite element modelling, analysis and results processing.
BC has spent about 40% of his time on this, with full time assistance from JBM. The intention of the effort is to develop CAE techniques on Single User Systems, with a view to their eventual incorporation into environments. The section acquired two SUN 3/160 M workstations at the beginning of the period, and thanks to the efforts of JBM on graphics interfacing we were able to port a large FE applications program from the ICL PERQ to a SUN in a few days. Agreement has been reached with Vector Fields Ltd of Oxford, which markets RAL FE software for electromagnetics, to develop jointly a new two dimensional potential modelling and analysis program for single user graphics workstations.
Stochastic sensitivity analysis of dynamic thermal models. CIB 86, Advanced Building Technology, Washington, Sep 1986. ADI
Covariance techniques in the detection of gravitational waves, in gravitational wave data analysis. NATO Advanced Workshop, 6-9 July 1987. ADI
Application of statistical techniques to the validation of multivariate time series simulators, 400 page contribution to the Validation Exercise Final Report, Sep 1987 ADI
Validation of dynamic thermal models, Energy in Buildings, Sep 1987 ADI
Building Energy Simulation, Energy in Buildings, Sep 1987 ADI
CAD*I Reports (unfortunately these are numbered in a manner similar to RAL Reports):
| RAL 0010/86 | 12 Nov 1986 | Report on visit to ISO TC184/SC4/WG1 | DT, JVM |
| RAL 0011/86 | 3 Dec 1986 | Syntax of the STEP Neutral File | JVM |
| RAL 0012/86 | 22 Dec 1986 | Syntax of CAD*I Neutral File | JVM |
| RAL 0001/87 | 12 Jan 1987 | Mapping of the new concepts of the Express language on the Physical File | JVM |
| RAL 0002/87 | 27 Mar 1987 | Specification for exchange of Product Analysis Data | DT, JVM |
| RAL 0003/87 | 21 Apr 1987 | Report on ISO Meeting at West Palm Beech, USA, 30 Mar-3 Apr 1987 | DT, JVM |
| 13 July 1987 | Report on ISO Meeting in London, 22-26 June 1987 | DT, JVM |
The following meetings were attended:
| Sep 4-12 1986 | Berkeley | EKS USA/UK | ADI |
| Sept 15-19 1986 | SERI (Colorado) | Validation Work | ADI |
| Sept 22-26 1986 | Washington | CIB 86 | ADI |
| Sept 25 1986 | Washington | W60 Building Performance | ADI |
| Sept 29 1986 | Washington | NBS, EKS Collaboration | ADI |
| Sept 30-Oct 2 1986 | Syracuse | Multivariate Statistics and Validation | ADI |
| Nov 3-7 1986 | Frankfurt | ISO TC184/SC4/WG1 | DT, JVM |
| Dec 2-3 1986 | Karlsruhe | ||
| Dec 11 1986 | London | British Standard AMT/4 | BC |
| Jan 26-27 1987 | Aachen | CAD*I Project Board and Review | BC |
| Jan 27-28 1987 | Aachen | CAD*I WG6 | DT, JVM, BC |
| Mar 19-20 1987 | RAL | CAD*I WG6 | DT, JVM, MM |
| Mar 30 - Apr 3 1987 | West Palm Beach | ISO TC184/SC4/WG1 | DT, JVM |
| Apr 27-28 1987 | RAL | CAD*I Project Board | BC |
| May 21 1987 | ICST | Robust Statistics | ADI |
| June 9 1987 | BSI | British Standard AMT/4 | BC |
| June 12 1987 | Polytechnic of the South Bank | Energy Flows in Buildings | ADI |
| June 22-26 1987 | London | ISO TC184/SC4/WG1 | DT, JVM |
| July 2-3 1987 | Copenhagen | CAD*I Project Board and Review | BC |
| July 6-9 1987 | Cardiff | Gravitational Wave Analysis | ADI |
| July 15 1987 | London | British Standard AMT/4 | BC |
The section has the following staff:
The section has grown from two to nine people during the last three years.
Two students, Phil Goodman and Janine Marsh left on 31 July 1987 after a year at RAL. This year there are three students - Karen Whitaker, Olivia Jane and Chris O'Mern. Also there is a long term visitor from University College Swansea, Dayal Gunasekera (DG).
The section is involved in Five Projects.
This has ten partners from five countries and 50% of the funding comes from the European Commission. Its objective is to extend the development of robust and efficient algorithms to simulate the behaviour of three dimensional semiconductor devices, to incorporate them in a computer code, and to compare the results against measurements on real devices. The project is funded for two years until April 1988, with the expectation of a further two years if progress is satisfactory.
CG is the Task Coordinator of Work Package 5, the Project Research Code. He is responsible for the specification and design of the software system, which is now being implemented at three sites. The software is divided into four parts, the Pre-Processor (Trinity College Dublin), Doping Profile Generator (University College, Swansea), the Analysis Code (RAL/GEC) and the Post-Processor (UCS). RAL is responsible for the kernel and for linking the modules together - initially this is using an extension of the neutral files used in the eddy current project, with the code implemented by KPD.
CJH and DG have integrated the modules from the different sites and are testing the program on various 3D benchmark problems. The project is being reviewed at the end of November by the Commission at which a demonstration of the working code will be made.
CG and CJH have also been involved in mesh generation algorithms which can be adapted to parallel machines. TKP is testing the GEC linear algebra package and integrating it into the RAL analysis code.
SERC is the Prime Contractor and RAL (CWT and ADB) is responsible for the management of the project as a whole. Vector Fields is contracted to provide CWT's services on one day per week at least until summer 1988, and from 1 July G A Lambert is assisting in the management of the project. At the last review in November 1986, the Commission requested some major changes which required a re-distribution of effort among the partners. This meant a great deal of discussion and visits to partners sites and Brussels before a new project plan prepared by ADB was produced in April 1987.
Project deliveries due from RAL at end of Period 2 (April 1987)
Work Package 5 Reports from RAL
C. J. Hunt, C. Greenough, A novel method for the computation of the Delaunay triangulation with a view to efficient use of parallel architectures. RAL-86-090
Consolidated Interim Reports are produced every 6 months for the Commission. Two reports were produced in October 1986 and July 1987. The Work Package 5 reports were edited by CG. The overall project reports are edited by ADB.
(N.B. The Reports are produced in four sections - Management Report, and three technical reports - 'Work Package 1, 'Work Package 2,3,4, and 'Work Package 5. The complete second Consolidated Interim Report was 3 inches thick!)
It is convenient to treat the RAL section of these two projects as one unit. There is also a considerable overlap with the Esprit Project in such areas as Command Decoding, graphics, geometric specification, mesh generation, etc.
The role of the Process Modelling Project 066 is to design and implement a flexible software system for modelling of semi-conductor processes into which other partners can slot specific modules. One of these is the device simulator being produced by RAL Project 034. RAL provides the binding elements, including the control program, the data base, graphics, etc. Three modules are provided by university partners Implantation (Kent), Diffusion (Reading) and Oxidation (Swansea). Each module must be capable of intercommunication via the database, and of being intelligently controlled through the RAL-provided interface. The Moving Finite Element mesh used by the Diffuser Module is generated with the Implantation module.
The considerable problems of software integration, validation, etc in 066 are the responsibility of JVA, assisted by RJF. JVA has recently organised a Software Week at RAL on July 6-10 with members from the three universities to help to integrate the software components together. JVA is also looking into future needs of process modelling. EMA is producing the device modelling module in 034, and spends a small amount of time on research in semi-conductor physics. RFF is interfacing the geometry module to the data base. CJH has worked on the designer and development of the geometric modeller and mesh generation. IMC is currently developing graphical software. CG is directing the RAL effort and is involved in design of the device simulator for 034, and design of the software shell and integration of the modules into it for 066.
| Alvey Device and Process Modelling Club, Edinburgh | 1-3 October 1986 | JVA, CG, CJH |
| 066 Software Integration Meeting, RAL | 18 November 1986 | CG, JVA, ADB |
| 034 Meeting, GEC | 21 Jan 1987 | CG, ADB |
| 066 Meeting, GEC | 29-30 Jan 1987 | JVA, CG |
| 034 Meeting, STL | 8 April 1987 | EMA, CA |
| 066 Meeting, Reading | 12 May 1987 | JVA, RJF, CG |
| 034 Meeting, RAL | 6 July 1987 | EMA, CG |
| 066 Meeting, RAL | 8 July 1987 | JVA, RJF, CG |
| 066 Software Week RAL | 6-10 July 1987 | JVA, RJF |
| 066 Meeting, Plessey | 23 July 1987 | JVA, CG |
These are produced quarterly. In addition there is an Annual Report. Specific reports produced by RAL are:
E M Azoff, T K Patel and C Greenough, Specification for a General 2D Device Simulation Program, Alvey Project ALV-DMP-12, Jan 1987.
E M Azoff and C Greenough, Alvey Device Simulation - Command Reference, Alvey Project, ALV-DEV-13, March 1987.
J V Ashby, Alvey/RAL Software Integration Week, ALV-DMP-19, July 1987
E M Azoff and R E Fowler, Alvey Device Modelling Kernel Release 1.0 The physical model # and numerical method, Alvey Project. ALV-DMP-20 due end August 1987.
CRIE has taken the leading role at RAL in this project, which involves both University and Imperial College, after CWT became part-time at RAL. This is a three year grant funded by Machines and Power Committee. Specific items in the programme have been carried out by NJD, CJC, KPD and CSH but most of the code is generated by CRIE.
CRIE represents the UK on the International Committee for Electromagnetic Workshops. He organised the first workshop at RAL in March 1986 and attended other workshops. A list is given at the end of this section.
Non-linear Transient Eddy Current Computation in 3 Dimensions - Project Overview C R I Emson Published in Eddy Current Seminar Proceedings, Editor C R I Emson, RAL Report RAL-86-088
Second Order Vector Potentials Applied to 3D Eddy Current Problems C R I Emson and C W Trowbridge Published in Eddy Current Seminar Proceedings, Editor C R I Emson, RAL Report RAL-86-088
A Simple Neutral File Definition C R I Emson Published in Electromagnetic Workshop Proceedings, Editor C R I Emson, RAL Report RAL-86-049
This activity has been given lowest priority and development has been very slow. Release 3, originally planned to be delivered to NAG in 1984, has been delivered and is undergoing final tests at NAG. The documentation will be completed by CG in early September 1987. IMC is implementing graphical output routines and providing support to the user community. The work on the library is part of the Application Software Programme funded by CFC.
(This excludes project meetings, which are listed with specific projects)
(NB The exhibit was requested by Central Office to highlight SERC's involvement with industry. The stand was shared with Vector Fields. ADB organised the loan of a VAX computer from Neutron Division and CAG provided a T4109 terminal to run the VF software. The exhibit with the same equipment loans was repeated at Techmart, NEC in November 10-15.)
(This excludes project documentation, which is listed under the specific project)
E M Azoff, Closed-form method for solving the steady-state generalised energy-momentum conservation equations, in Procedures of NUMOS I Workshop, P25 Los Angeles, Boole Press, Dublin (1987) and in COMPEL 6, P25-30, 1987.
E M Azoff, Generalised energy-momentum conservation equations in the l6relaxation time approximation Solid-State Electronics, 30, pp 913-917, 1987.
Results From The 3-D Eddy Current Package CARMEN C R I Emson Electromagneto-mechanical Interactions in Deformable Solids and Structures, North Holland, Amsterdam 1987, P163-168, Editors Y Yamamoto and K Miya
Recent Developments in the Computation of Eddy Current Effects C W Trowbridge and C R I Emson Electromagneto-mechanical Interactions in Deformable Solids and Structures, North Holland, Amsterdam 1987, P15l-l62, Editors Y Yamamoto and K Miya
Methods for the Solution of Open Boundary Field Problems C R I Emson To be published in IE E Proceeding, Part A, 1987
The section is responsible for the support and development of Single User Systems for Engineering Board researchers and for the Alvey Programme; graphics on ECF machines; and text processing on ECF Unix machines. Some of these activities are also carried out for the divisional service, IDUS.
This team (led by PK) is responsible for support of centrally purchased and maintained Single User Systems funded through Engineering Board committees and the Alvey Programme. During the year, the equipment has been for a rapidly increasing population of Suns and, as grants come to an end, a declining population of PERQs.
During the year, there have been a few staff changes. Fran Childs was in the team in September 1986, but was gradually taking on more work for the ECF as a whole. She therefore transferred to Geoff Lambert's section.
MDP joined from the ASO Training Scheme early in the year and MC joined the laboratory on 29 June 1987 after what could be a record for a work permit delay (he was originally interviewed in May 1986!). KML gained promotion to the post of Head of SUS User Liaison in May and, assisted by MC, WJH and MDP, has most of the user support responsibilities in the team.
The first contact a user has with the Support team is usually when he/she is preparing a grant application. Although a proportion of grant applications fail, seeking advice is encouraged at this stage, so that fewer complications occur at the critical later stages. PK does this work. He is also expected to comment, when applications are actually received by a committee. This year, at the last round, all the comments for a particular subcommittee (Computer Science) were processed in a single visit to Swindon Office (others took part, but PK looked after the SUS requirements). This was successful as far as it went, but needs to be extended to other EB committees.
The central purchase arrangements for Suns have been in place the whole year and are running more smoothly. However the difference this year is the much larger number of machines. Altogether there were over 200 installed during the year, including 33 at the University of York. The sheer numbers require some effort in organising purchases and maintenance contracts and some streamlining of this is needed. For SERC grants, Central Office order directly from Sun. This relieves the Support team of some administration effort, but difficulties can arise due to the team simply not being informed when a Sun is installed.
The number of supported machines is (as at 31 August 1987):
333 Sun 3's
54 Sun 2's
48 PERQ 2's
28 PERQ 1's
The target for the end of maintenance on PERQ 1's is end September. Only a small number of grants that were originally equipped with PERQ 1's continue beyond that date. A number of other PERQ 1' s were allocated to a variety of places through a variety of funding budgets. These people have been contacted by the Support team over the last few months and satisfactory arrangements have been made. Grant holders that continue to use PERQs after the grant has expired can make use of the coordination and distribution services provided by Queen Mary College and funded by the Computer Board. (KML,MDP)
A regular six-weekly progress meeting with Sun has been begun and new arrangements for the maintenance contract will begin on 1 October. Under the new arrangements, fault reporting (whether for software or hardware) will be through RAL and this will enable the Support team to have up to date information on the pattern of faults. Also RAL will have early copies of Sun software in order to advise Sun on software distribution.
A database for Sun 3's was set up during the year. It was found that information from several completed forms from different parties (SERC at Swindon, Sun, the users, etc) was needed in order to compile the records for any particular Sun. Most of the SUS Support Team were involved in the catching up exercise and Janet Smith is now responsible for the database upkeep.
The SUS Support office telephone has been staffed for most of the year by WJH.
One Common Base User Forum was held (KML, LJJ-N) before it was absorbed by the Engineering Computing Users' Group.
Several software distribution rounds have taken place during the year.
Sun are responsible for distributing the operating system and most users are now up to version 3.2. The Support team distribute software added by RAL (or by contractors, such as University of Kent). Software distributed this year from RAL (by KML, MDP, WJH, LJJ-N) includes:

LJJ-N produces installation scripts so that the user can move the software onto his/her Sun in a reasonably automatic way. Further basic software is being negotiated, of which the first example is Nag (the Nag library and and Nag Graphics) (PK, KML - also JRG, DCS).
On PERQ, there has been a maintenance release of operating system software for both PERQ 1 and PERQ 2 (PNX 5.3), which the Support team has distributed. In addition, a new optimising Fortran compiler, WW with Pascal and Fortran and Kent tools have been distributed (KML, WJH, MDP). The copying has been in co-operation with Queen Mary College. KML is setting up a machine (a Sun 2) to handle software distribution via the network. It will also make available up to date information about services available to users. Progress has been made, but some equipment is still awaited. It is expected that this will make software distribution far more convenient in the future.
Some performance testing has been carried out this year.
It is anticipated that performance testing will become a far more significant activity in the coming year.
Currently no Sun we have produces colour permanent copy. Most equipment is designed to be attached to display equipment of lower resolution. The two main classes of output are photographic film (35mm or other) and colour output on paper or foil. A survey has been carried out and some demonstrations of colour output on paper and foil have taken place (KML with advice from DCS). The aim is to produce a report to guide future divisional purchases and to assist in advice to prospective grantho1ders. Some equipment that was spotted at Siggraph will be investigated before the report is produced.
During the year, SUS Support moved from offices in R32 into an open plan area. Although some aspects of the original scheme were not funded (for example, a small support meeting room for visitors), the open plan area has worked reasonably well for support activities, where information is frequently passed between members of the group (planning by PK and FMC with input from everyone).
The PERQ disc server has been put on the Ethernet. It is used to hold supported PERQ software for the support team and as additional work space for internal PERQ users (KML). This usage will need to be kept under review as PERQ activity drops further.
Support for the Transputer Initiative has been provided. MDP has tested and installed software on equipment in the loan pool.
During the early part of the year, this part of the section which was to become the Basic Software Team increased in size with the addition of several new faces. Andrew McDermott joined from the ASO Trainee Scheme, David Johnston joined from the ICL PERQ Business Centre and in December Pre drag Popovic from Yugoslavia finally received his work permit and was able to start. Dale Sutcliffe transferred from Central Computing Division Graphics Section on 3 November to lead the Team and in December Ruth Kidd also transferred from the same section. She brought with her the ICF Graphics work, so drawing together all the Engineering Board funded graphics work in the same team. This, together with the existing members, made a team of ten people by the end of 1986.
Early in 1987 it became necessary to restructure the team to carry out more effectively the tasks it had been assigned. The team was divided into three parts, namely ICF Graphics; SUS Graphics and Window Managers; and Text Processing and System Development led by Ruth Kidd, Trudy Watson and Jan Malone respectively. To reflect the work of the team more accurately, it was renamed the Basic Software Team, all the work being concerned with providing the basic software that users expect to find on a good system.
The purpose of the team can be summed up as developing, providing and supporting widely usable basic systems providing common interfaces on which higher level software and applications may be built. As time progresses, expectations will increase and the scope and functionality of basic software will increase.
Further staff changes took place during the year. David Johnston (DJJ) transferred to join the transputer coordinator team, and though Duncan Gibson joined the team in his place from Software Engineering, he was about to leave as this report was being written. Andrew McDermott (APMcD) transferred to the Communications team in Infrastructure Group in August 1987 to work on local area networks.
At the beginning of December 1986, the graphics work on the Primes and GECs, referred to as ICF graphics, moved from Central Computing Division when RMK transferred to Informatics Division. The opportunity was taken to place the whole of the Engineering Board funded graphics work together in Basic Software Team. RMK now leads a small team of PLP and (for most of the year) APMcD.
The RAL GKS implementation project became a joint project of CCD and ID following the transfer of ICF Graphics - the master source of RAL GKS is held on Prime A. (NB: regular project meetings are held with CCD to monitor progress). The original implementation was of the Draft International Standard version of GKS and plans had previously been made to upgrade it to the IS version of GKS in collaboration with the Computer Board GKS Support Team who support RAL GKS (as GKS-UK) in the Universities. In late 1986 DCS and RMK planned the upgrade with the GKS-UK Support Team culminating in a week of intense activity at Ross Priory on the shores of Loch Lomond in January 1987. The week was successful and the nine participants emerged at the end of the week with a completed set of edit files for GKS and all overweight!
The GKS-UK Support Team executed the edits and a joint period of testing followed. During the testing, the NCC validation suite was issued on beta test. RAL became a beta test site and was able to test the validation suite and RAL GKS simultaneously. Faults were found in each but overall the honours were even! All the workstation drivers in the RAL set were upgraded to IS status. The new master source was assembled on RL. PA and distributed to the SUN, CCD and the GKS-UK Support Team in July. This means that RAL GKS now matches level 2b of the International Standard and implements what will become the International Standard Fortran binding. This version is known as RAL GKS 1.00.
As well as development of the master source of RAL GKS, work has been done on its installation on different machines. RMK completed the installation of RAL GKS 0.10 (the DIS version) on the GEC in time for the ECUG meeting in April. This was well received by the user meeting.
With the change in recommended Fortran compiler from FTN77 (Salford) to F77 (Prime) on the Prime and the incompatibilities between the two, it became necessary to provide an F77 version of RAL GKS. This was completed and the library built using BIND to provide a shared library. The result was faster execution and smaller run files, but restricted the ability to add additional workstation drivers without rebuilding the library. Temporarily the shared library prevented the user replacing the error handler, though this last problem has now been solved.
Good progress has been made with configuring RAL GKS 1.00 for the Prime and it should have been released by the time this report appears.
Provision of all requested workstation drivers continues to be a problem. However, a Printronix (a dot matrix printer) driver has now been added to the portfolio (PLP). Based on a VAX specific one from Starlink, the new driver is portable and uses a character heap in RAL GKS, a feature always anticipated but not before implemented. To assist in the provision of future workstation drivers, RMK gave a seminar on writing a workstation driver to CCD and ID staff.
A terminal from Ferranti implementing a logical GKS workstation was evaluated by APMcD. It has a mixture of good features and some peculiarities, and it was decided not to purchase the device.
The NAG Graphics Chapter Mk2 became available for the Prime. It was installed for use with both GINO-F and GKS by APMcD. A NAG Graphics Mark 2 library for use with GINO-F was also released on the GECs. This library will assist users to transfer their graphics applications from GKS to GINO-F.
TAW leads this small team which is responsible for graphics on the Single User Systems (currently PERQs and SUNs). Currently, this small team also looks after graphics on the Unix MUMs (Pyramid and VAX). The team members are JH, MJP and PJWR.
By September 1986 it had become apparent the SUN's GKS had fundamental problems which were not going to be cured with a few bug fixes. There was an urgent need for GKS on the SUN. At the same time the Computer Graphics Unit at the University of Manchester had experienced similar problems with SUN's GKS and had entered into a collaborative agreement with SUN to sort out the problems. After discussion with all the interested parties, the best solution to all these problems appeared to be to install RAL GKS on the SUN and to implement a workstation driver for the SUN screen, with work shared between the Computer Graphics Unit at Manchester and Basic Software Team at RAL. The work was planned in a number of stages and was to use WW to access the SUN graphics facilities with a GKS workstation mapping onto a new window.
The first version was essentially complete at the end of March (TAW and PJWR) and Tony Arnold (UM CGU) gave a presentation on the work to the SUN UK User Group in April. A second version incorporating colour, extra input devices, and using RAL GKS 1.00 (the IS level 2b version) is well under way and will be complete before SUN OS 4.0 incorporating NEWS is available. At that time the interface to the SUN will need to be examined.
As the first version was completed, a completely new GKS appeared from SUN for beta test. Some testing was done (TAY) and this time the implementation appeared basically sound. It was a level 2c version but as yet the level c input features have not been tested. It may be a useful way of providing this facility on the SUN in the future.
York continued on the assessment of GKS-3D from GTS-GRAL. Some of the problems were solved on moving from SUN OS 3.0 to SUN OS 3.2. It is understood that the latest version works within a window rather than taking over the whole screen but delivery is still awaited. In order to gain more experience with GKS-3D an EMR contract has been placed with Owen Mills at the University of Manchester to carry out an assessment of GKS-3D on a SUN, in the area of molecular graphics. An order has been placed for limited number of licences for GKS-3D.
With more direct control over the release of RAL GKS master source, it became easier to coordinate releases of RAL GKS on the Unix MUMs. RAL GKS 0.10 was successfully installed on the Pyramid and Vax (BSD4. 2) including reimplementing the system interface in the light of experience and to incorporate extensions with this release. (PJWR).
Assistance was given to those producing the RAL GKS 1.00 master source in detecting undeclared variables using both the SUN and Pyramid Fortran compilers. This work was helped in the installation of RAL GKS 1.00 on the UNIX MUMs, though this is not yet complete.
In line with the aim of providing common basic software across the ECF machines, steps are being taken to provide the NAG Graphics Chapter Mk2 on top of GKS on the SUNs and Pyramid. NAG have been encouraged to carry out these implementations and were lent a SUN3 in order to test the Graphics Chapter with RAL GKS. They made good progress but there are a few items to be sorted out. The implementation on the Pyramid is also nearly complete.
Testing of Visual Engineering's GKS was completed following delivery of the full Graph Cap system. This latter system, designed to reduce driver writing to filling in a table, worked reasonably well but had some peculiarities. A driver for the Sigma 5684 was nearly completed but this was output only - input was not attempted. There were also some shortcomings in the language used to describe the device. The implementation seemed satisfactory though the C binding was not the latest one (this may have changed since we received the software). (APMcD, PJWR)
Some experience was gained with the GKS from Precision Visuals on the SUN and a report was produced (MJP).
A Postscript driver for RAL GKS is an important requirement, given the use of Office Laserwriters on the SUNs and the increasing use of Postscript in text processing. Work has started on a Postscript driver received via Starlink and this will be made to adhere to the project conventions and to be machine independent (MJP).
Work was completed to provide access to WW from Pascal and Fortran (JH). Some problems occurred in keeping track of new versions of WW but a successful outcome was achieved when Pascal and Fortran interfaces were completed and distributed which matched the C version of WW distributed at the same time.
With the increased use of single user systems with high resolution displays, window systems are receiving more attention. Experience has been gained with both SUN News and X-windows during the year.
MJP coordinated the beta test of SUN News with the Universities of Sussex and Kent and QMC, with replies being received from the latter two. The first beta test version left a lot to be desired, while the second beta test though somewhat better did not match the expectations of a released version which it turned out to be!
MJP also installed X-windows versions 10.3 and 10.4 and the beta test version II, the latter still being in progress. He produced a report of this experiences but a future strategy still has to be agreed.
Following the purchase of a Silicon Graphics Iris 2400 for evaluation at the Abacus Unit at the University of Strathclyde, it was decided to do a fuller evaluation of high performance 3D workstations. Currently on loan are an Apollo DN580, and a SUN3/260 (to be upgraded to a SUN4) and a Hewlett Packard 350 SRX is expected shortly.
Software was obtained from the University of Strathclyde for implementing on all the systems but is is not clear that this is a good test of 3D hardware. Some work on synthetic benchmarks has also been carried out but no results are available yet (JH). Harwell are also doing some work in this area to display results from the Cray and discussion of their experiences have taken place.
With A S Williams, MJP has carried out a survey of User Interface Management Systems on the market. He will be presenting a paper on his findings at the ECF Workshop on UIMS in September 1987.
With A Conway, MJP has been investigating visual illusions on displays (see the HCI Section report for more details).
This small team, led by Jan Malone, is responsible for text processing and specific items of systems development that the team is called upon to do. For a set of unconnected reasons this small team has seen the most change in personnel. At the beginning of the year Jan Malone was assisted by David Johnston but following the approval of the Transputer coordination programme he transferred to that project from 1 April. His place was taken by Duncan Gibson transferring from Software Engineering but he is about to leave RAL as this report is being written.
The text processing work is carried out both for the ECF and on behalf of IDUS. On the Suns, it is also carried out on behalf of Alvey, Infrastructure. It is believed that the requirements do not differ enormously and that the same software can be used to satisfy each of these. A text processing plan for the division was approved at the beginning of the year (JRG). Whilst the formation of IDUS has changed the details in some respects, the overall plan remains valid.
The first components of forming a uniform text processing service are the provision of DWB 2.0 and Transcript 2.0, to drive the office laserwriters, on the Pyramid, under both universes, and the SUNs.
DWB and Transcript 2.0 were provided by Pyramid under the att universe but not the UCB universe. The Systems team in Infrastructure Group are to provide access to this software from the UCB universe.
DRG completed the implementation of DWB 2.0 on the SUNs, before he left, and Transcript 2.0 has just been received from SUN. DWB 2.0 will occupy a temporary position on the SUNs initially to enable users to change from using the existing troff software which has names in common with DWB 2.0, but cannot be moved because of lack of sources. After a suitable time the old software will be removed and DWB 2.0 transferred to its usual home.
Macro support for DWB 2.0 is currently under consideration and a survey on usage is about to be carried out in conjunction with Operations/Support section.
Transcript 2.0 has also been provided for the PERQ. The documentation is about to be completed. As no laserwriters are connected directly to a PERQ the despooling software has not been implemented (JCM).
It has become clear that not only has the Sun Pascal compiler not been validated as conforming to ISO Pascal, but has actually failed some of the validation tests. The importance of providing ISO Pascal has long been realised and a programme to evaluate third party validated ISO Pascal compiler for the Sun has begun. The compiler from Edinburgh Portable Compilers has been validated. Others will be tested before a decision on future provision is made (DJJ,JCM).
With the need for users to transfer programs from PERQs to SUNs, some effort was put into providing transition aids. Depending on the software used, transition was not too difficult for some where the software was already available on both machines. For those using graphics system calls on the PERQ, an emulation package was written for the SUN. Documentation on its use and the restrictions was also produced (DJJ).
Some effort was put into providing access to Sun and VAX filestore (including NFS filestore) from a PERQ/2. Investigation of providing blue book FTP over ISO TP4/LLC1 which existed on the PERQ/2 (Jan Malone) was carried out. Alternative strategies were also investigated but the final solution was to provide Newcastle Connection using the minimal UDP/IP driver on the PERQ provided by Robert Stroud at Newcastle. Chris Crampton in RCI Section completed this work.
As a result of the operational requirement issued in August 1986 and the tender issued in November 1986, Sun were chosen for the small cluster of workstations and Pyramid for medium and large clusters, although it is expected that the boundary may be somewhat blurred at times. Bob Day has been heavily involved in this activity, especially the communications aspects.
The first system external to RAL is going in at Warwick as an intended replacement for the ICF Prime.
JRG has attended two ISO meetings, one of them the working group on computer graphics, ISO JC97/SC2l/WG2. JRG has concentrated on the programming language interfaces (or language bindings) and as a result of these meetings, the Fortran and Pascal bindings of GKS are now standards and GKS-3D and PRIGS language bindings are making progress. JRG is the ISO document editor for the Fortran language binding of GKS-3D.
The University of Kent have an EMR Contract from the ECF to produce software tools for Single User Systems. In the past year, emphasis has been on refining the tools and porting them to the SUN.
J R Gallop: User Interface Management and Graphics Standards in Information and Software Technology, May 1987.
(M R Sparks and) J R Gallop: Computer Graphics Language Binding: Programmer Interface Standards in Computer Aided Design, October 1987 (to appear).
M J Prime: User Interface Management Systems - a Current Product Review paper produced for ECF Workshop on User Interface Management Systems, September 1987 (to appear).
SUN USER NOTES 5-10
PERQ USER NOTES 10,11
COMMON BASE TECHNICAL NOTES 36-85
GKS PROJECT MEETING NOTES
| NCC Seminar on TOP (DCS spoke on Graphics Standards) | NCC | Oct 86 | DCS |
| BCS Displays Group: Workstation Publication Systems | Oct 86 | DCS, JH | |
| BCS one day meeting on User Interface Management Systems | London | Dec 86 | JRG, JH, MJP |
| ISO TC97/SC2l/WG2 Rapporteur Group on Computer Graphics Language Bindings | Fort Collins, Colorado, USA | Jan 87 | JRG |
| usr/group seminar on desktop publishing and document preparation under Unix | Feb 87 | DCS | |
| NCC: National Technology Conference (JRG gave presentation on "Current Developments in Workstations") | Brighton | Feb 87 | JRG |
| European PERQ User Group | RAL | Mar 87 | Many |
| CHI 87 | Toronto, Canada | Apr 87 | MJP |
| Sun UK User Group | Manchester | Apr 87 | DCS, PJWR, TAW |
| NeWS Seminar | London | Apr 87 | MJP |
| Eurographics UK | University of East Anglia | Apr 87 | DCS, PJWR, DCS, TAW |
| BSC Displays Group: Parallel Processing for Displays | May 87 | DCS, JH | |
| Postscript Seminar | London | May 87 | DCS, JH |
| Seminar on Graphics Standards | London | May 87 | DCS (Chair) |
| ISO TC97/SG2l/WG2 Working Group | Valbonne, France | May 87 | JRG |
| ICS Computer Graphics: A comprehensive introduction | London | Jun 87 | APMcD, PLP |
| Sun UK User Group | London | Jul 87 | TAW |
| NATO Study Institute - Theoretical Foundations of Computer Graphics | Lucca, Italy | Jul 87 | JH |
| Siggraph 87 | Anaheim, California, USA | Jul 87 | RMK, DCS, CAD |
| Workshop on the future of NAG Graphics | Leicester | Aug 87 | JRG |
| Eurographics 87 | Amsterdam | Aug 87 | KML, PJWR, DCS |
| MSc Course on Computer Graphics at Middlesex Polytechnic (one day per week) | London | Ongoing | JH |
Members of the section have also attended various short courses during the year.
The purpose of the Operations Sub-section is to provide operational services, on whatever hardware, to the Engineering Computing community, to the Alvey community, and to the Division as a whole. In much the same way, the User Support Sub-section provides assistance and advice to users of these facilities.
The staff in post at September 1987, with three new permanent members recruited and two sandwich students taken on for six months each, is as follows:
(Prior to the divisional reorganisation of 1 November 1986, Cyril Balderson was in charge of Operations and Geoff Lambert was in charge of Support. Tony Lowe was also in Operations.)
During this period, both PDA and MJL gained promotion to HSO.
Apart from supervising the activities of the staff above in their work and personnel management, MEC has mounted the SLICE package on Prime, defined and implemented the functions of a system administrator, and been involved in the setting up of the Division Unix service becoming Service Manager.
MEC is Chairman of the Unix Service meeting held monthly, Chairman of the Prime Progress meeting held at 6-8 weekly periods and Chairman of the GEC availability meeting held every 3 months.
The past year has seen the emergence of the System Administrator for the Engineering Computing Prime service and an associated set of duties and responsibilities. These have become an additional part of RP's workload and include full responsibility for resource management on all the RAL Primes. Other work which has arisen as a result of this concerns the need to provide accurate availability figures for the RAL machines. To this end he has been involved in discussions with CCD with a view to producing a specification and mechanism to provide such information via the Incident Report form used by CCD. Other activity has resulted from a decision reached by the Prime Coordination Committee to conduct a files tore audit of the RAL systems. This involves setting up information files describing software held in certain system directories, and maintaining these files. He has done extensive investigation and written a discussion paper to facilitate its introduction.
RP has continued to maintain close contact with the Operations staff of CCD responsible for operation of the Prime systems. In particular he has been involved with major hardware faults affecting RL.PF, continuing in his role as first point of contact for Prime Computer (UK) field service management. With the removal of the systems support staff at RAL he has found more demands placed upon him when system software problems arise. Another problem, and one as yet unresolved, concerns the software for files tore backup used on all the RAL machines - this stopped working properly after a Primos update and he is now coordinating activity to establish the causes and then move towards the introduction of a later, correct version.
RP is secretary of the Prime Progress Meeting held at 6-weekly intervals, alternating between RAL and Prime at Hounslow.
PDA has spent a great deal of her time this year working on, and generally completing, special projects.
The merger of RL.PG and PL.PI into one machine was planned and completed by PDA involving the re-organisation of the filestores, machine configuration and the preparation of the SAD and Accounts database to reflect the requirements for handling the charging on the new machine.
This year PDA has handed over resource management tasks to local and remote site managers. A visit has been made to each site to present the database and to instruct the managers in its use. The Resource Management database which has been set up, to allow the managers to carry out their own resource management, has been generally accepted without too many problems. She needs to be available to consult with managers on problems relating to their new role and this is still very time consuming.
The streamlining of the Accounts database is still an outstanding project but much discussion has taken place and a draft paper produced, detailing the procedure for handling this database and the recording of the information. The ultimate aim is to make the Resource Management database interlink to the Accounts database. This will provide an automatic system of recording information which should reduce considerably the amount of manual effort that is currently required.
PDA has produced statistics and performance analyses as the need has arisen. Her experience has also been useful in relation to problems with the accounting procedures.
PDA is secretary of the internal Prime Co-ordination Meeting which is held at intervals of 6-8 weeks.
Primos Rev20 will be introduced on all the RAL Primes soon and this particular revision requires a conversion of the entire files tore . Both RP and PDA have done some preliminary planning to perform this.
ACD joined RAL in April 1987 from Technical College with little practical computing knowledge and is thus under training from RP. However he is able to assist in some of the system administration functions. He is also providing operational cover, such as dumping, for the development Prime RL.PD and the GEC RL.GK for MJL.
RT joined this Sub-section at the beginning of this reporting period as network system administrator for the SUN workstations within the Division. This includes the servers which provide user files tore accessible from any workstations with no local disk. There are 17 such diskless workstations and 20 with disks. The Ethernet LAN upon which clients and servers rely also includes the Division's MUMs, and the four laser printers attached to SUNs are available to them as well.
The network has become a service during the year and RT is in constant contact with users, and with owners of client machines. He has devised some of the tools, techniques and procedures used in administrating the service. These include the use of rdist to maintain file system mounts and local features across all the SUNs, the systematic incorporation of new users and new workstations, and a single point of contact for SUN hardware maintenance.
Particular events over this period have included the installation of SUN release 3.2 across the system, the addition of a further disk drive, the addition of the third server and several disked and diskless clients, the extension of NFS to the Division's MUMs, the transfer of some MUM load, eg news, laser printers, to the SUNs, and the introduction of automated server filestore dumping.
The network is expanding and he has been participating in planning the various phases in introducing the Yellow Pages shared user and password database.
IV is the system administrator for the Systime VAX rl.vd which, apart from being an Alvey Infrastructure machine is also the main Divisional mail machine and the host for the NeWS system. System administration has meant the investigation of machine performance problems, and peripheral problems. It has also included responsibility for filestore security through backups and installing software updates. Since July she has taken over system administration responsibilities for the Pyramid rl.pyr-a, the Pyramid workcentre nfs4, and the Software Engineering VAX rl.vc.
IV has participated in the conversion of rl.vd into the single filestore controlled by NFS which also includes rl.pyr-a, nfs4, three SUN fileservers, and the SUN single user systems. This is now used to provide all the user filestore for the Division's Unix service.
IV has written documentation for the local auto dump procedure which is being used by the CCD operators when performing overnight dumping of the VAXes and Pyramid.
IV is the local administrator of the News system, the worldwide bulletin board operated over USENET. This work involves the monitoring of disk space used by the system, the creation and removal of news groups, and liaison with other News administrators. She also administers the Divisional Arpanet registrations at the UCL gateway.
In a similar capacity to IV, AMJ served as system administrator for rl.vc and rl.pyr-a, and participated in the mounting of NFS upon the latter machine, until July. He was also responsible for the R1 Machine Room which entailed the planning for the arrival of new computers and the disposal of surplus equipment, the arrangement for services, such as electrical supplies, within that area, the co-ordination of the movement of computers, and the general arrangement of equipment. This has a bearing on his position as a building warden and the Divisional Safety Representative.
Two particular jobs in this period have been the evaluation of a Spiderport and the writing of a VMS format tape for use in Spain.
AMJ is secretary of the Unix Liaison Meeting which meets every 2 months.
Since July, when the Computer Applications Group of Technology Division merged with ID, he has been paving the way for a smooth merger for the two dozen or so people involved in the move. This has meant talking to each of them individually to find out what equipment they already have, what facilities they are using, and what they would like to have in becoming part of the Division's Unix service. Anticipating the need for workstations and networking facilities, he has been working sometimes with Tony Lowe to gain knowledge in this field.
AJ provides assistance to the system administrators and performs general machine operations. This is a long list which includes:-
LJR joined the ECFE on 27 April on a part-time basis, 3 days/week, but it was decided to transfer her to Operations on 24 July as a more suitable place for training.
In order that the users can always receive assistance quickly, the aim has been that all members of the Sub-section should be able to support all machines. In practice, BAA supports Unix, MJL supports GEC and PCP supports Prime but all are capable of supporting other machines to some degree.
On the Prime, BAA has put up the long integer F77 version of the main NAG library fixing a bug in one of the routines. On the Pyramid, he is mounting Mk11 of the main NAG library since the version supplied by NAG does not work.
BAA is secretary of the monthly held Unix Service Meeting.
The staffing problems within GEC Systems Section became worse with the resignation of Neil Davidson and the transfer of Shirley Wood to JNT. An emergency meeting of the site managers agreed to abandon the intended upgrade of the operating system to version 4.17. Instead the current version was frozen with the known problems accepted. C D Rust (CDR) of GEC Systems Section and MJL continued with overall GEC support of ECF systems until April when CDR was moved. Since then MJL has taken sole responsibility for the day to day running and system management. He has produced and distributed revision to Volumes 1 and 2 of the Reference Manual, fixed all known bugs in KERMIT and made some improvements to the HELP system.
MJL is organiser and secretary of the GEC Manager/User meetings held twice a year, and secretary of the GEC Availability meetings held every 3 months.
PCP is responsible for the development, maintenance and operation of the Resource Management and Accounts databases. The former provides an interactive facility for site managers to enter grant and user details, the latter contains actual usage information for all users of ECF and TD Primes and GECs. Statistics are produced for Management and for publication, and bills are produced for Finance. He continues to develop these services in liaison with PDA. He performs the updating of software on all the RAL Primes, keeping the users aware of intended and actual changes.
PCP is organiser and secretary of the Prime User meetings held twice a year.
Two sandwich students from Brunel, namely B J Edwards (BJE) and P Sausman (PS), joined for 6 months each from 13 April. Working under BAA, they have produced an IDUS paper, introducing new members in the Division to the UNIX services available. With guidance and assistance from PDA and from UMIST, PS has been rewriting the Prime performance analysis package. BJE has been involved in benchmarking versions of Primos.
MJK joined on 22 June to support Unix users and is currently going through a training period.
The work of JRS covers both the Operations and the Support area and both the ECF and the Unix Service facilities. This is because she maintains and updates the many databases used by all concerned. Those which have been of most use in this period have been:-
JRS has also liaised with many locations regarding the disposal of old ECF terminal on loan to them, and reporting those accepted to RAL Loan Pool.